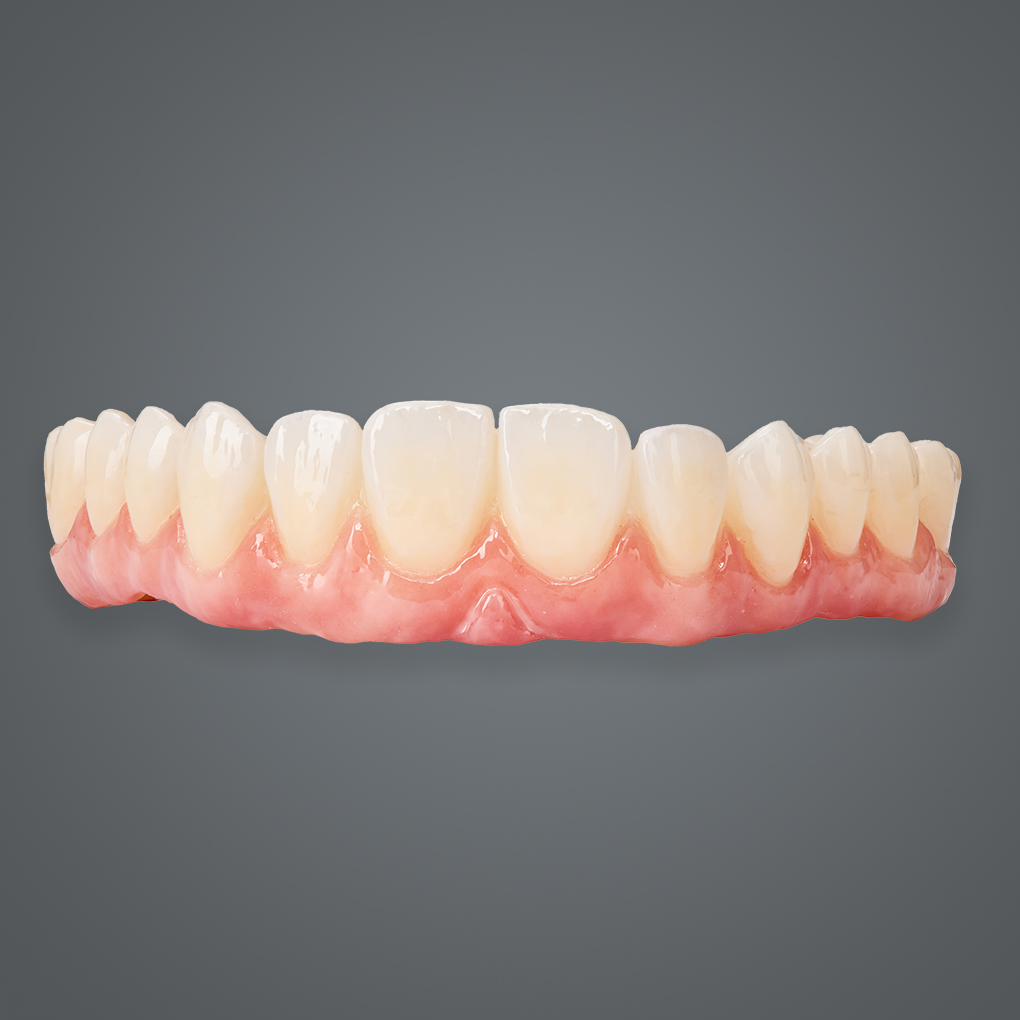
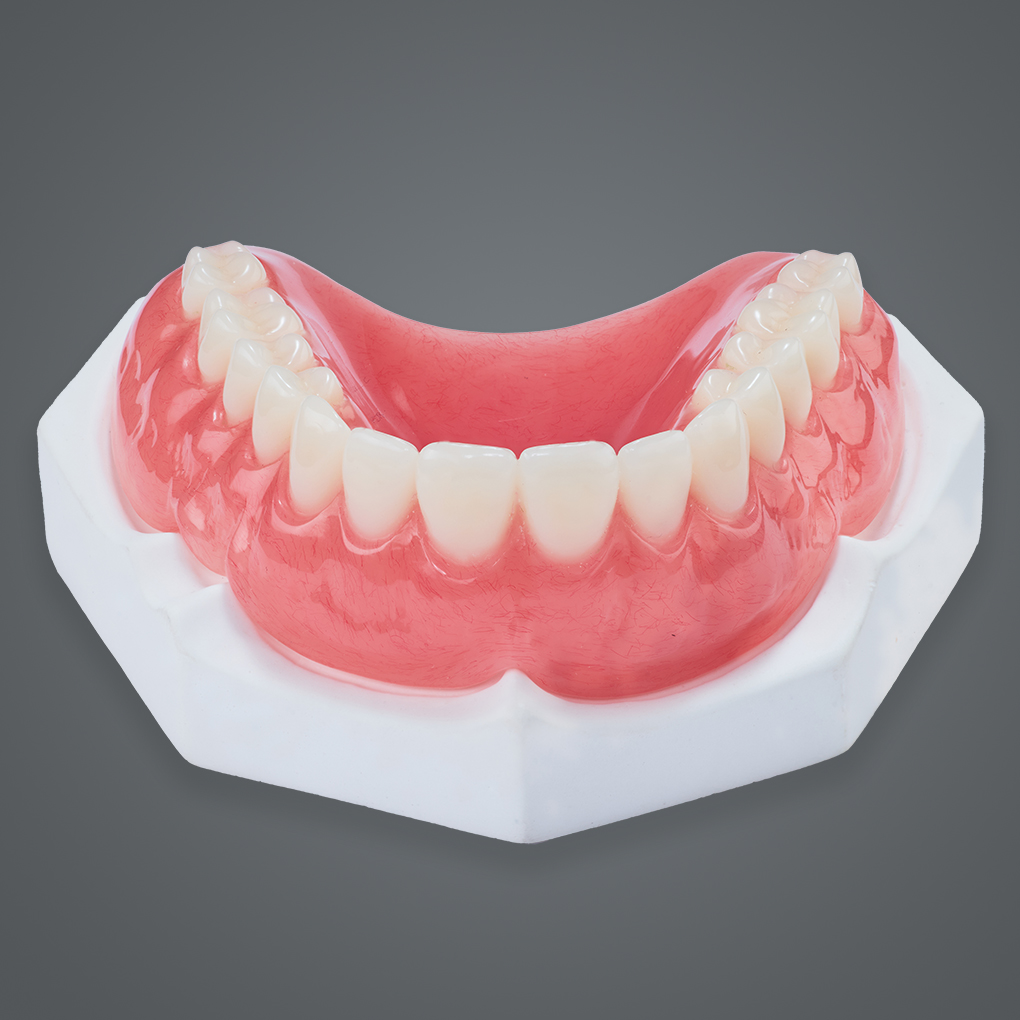
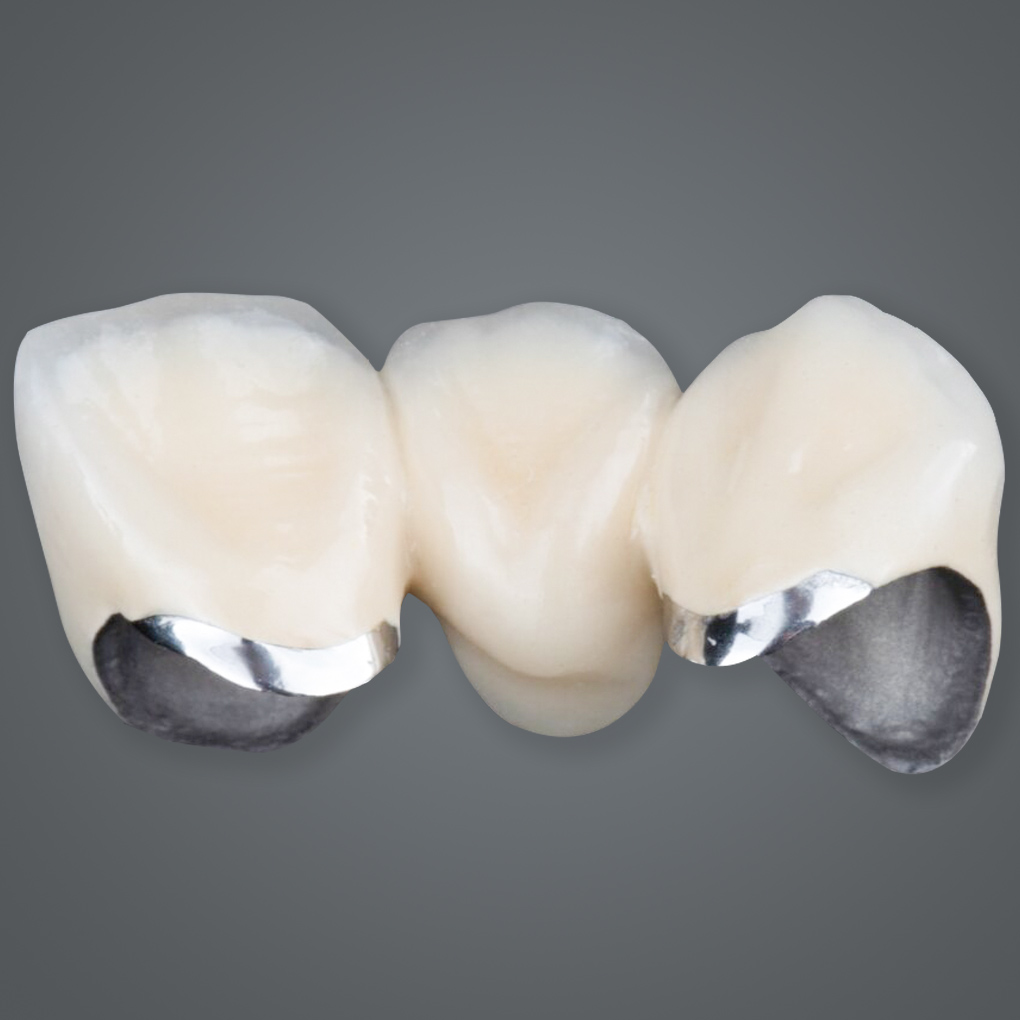
In today’s fast-paced dental industry, optimizing solutions for crown and bridge has become paramount. Zirconia has become one of the most sought-after materials for crown and bridge, and understanding its variations is essential for delivering results that meet both clinical requirements and patient expectations.
Here, we’ll explore the key differences between Monolithic Zirconia and Esthetic Multilayer Zirconia from a dental lab’s perspective.
Contents
1. Introduction to Zirconia in Dentistry
Zirconia, or zirconium dioxide, has revolutionized dentistry as a biocompatible and highly durable material. Its versatility makes it an ideal choice for crafting crowns and bridges that meet both functional and aesthetic requirements. For us in the lab, its versatility allows us to tailor restorations to specific clinical scenarios, ensuring that every case meets the demands of both dentist and patient.
1.1. The Popularity of Zirconia for Crown and Bridge
Dental practices across the United States are adopting zirconia for restorations due to its ability to combine strength, longevity, and beauty. Outsourcing zirconia crowns and bridges to specialized dental labs can further enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure consistent quality. Among zirconia materials, Monolithic Zirconia and Esthetic Multilayer Zirconia offer distinct advantages depending on the case.
2. What is Monolithic Zirconia?
Monolithic Zirconia is a single-layer material that is milled from a solid block of zirconium dioxide. It is valued for its durability and functional performance, making it a staple in our lab for certain restorations.
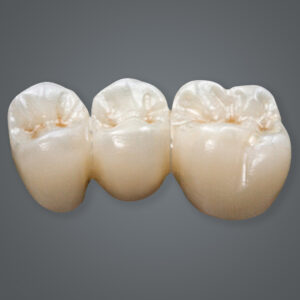
2.1. How Monolithic Zirconia is Made
Using advanced CAD/CAM technology, dental technician design and mill monolithic zirconia restorations to precise specifications. After milling, the restorations are sintered at high temperatures to achieve their final strength and translucency.
2.2. Key Characteristics of Monolithic Zirconia
- Strength: Resistance to fractures and wear.
- Durability: Suitable for posterior crowns and bridges where chewing forces are high.
- Low Aesthetics: Its lower translucency makes it less ideal for anterior restorations where appearance is critical.
3. What is Esthetic Multilayer Zirconia?
Esthetic Multilayer Zirconia, as the name suggests, is a layered version of zirconia designed to mimic the natural gradation of human teeth. This material incorporates multiple layers of varying translucency and color to achieve a more lifelike appearance.
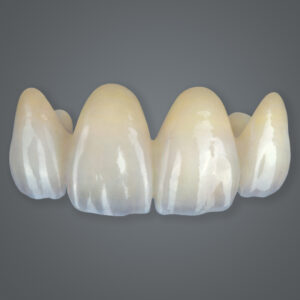
3.1. The Process Behind Multilayer Zirconia
Multilayer zirconia blocks consist of multiple layers, each designed to replicate the natural properties of dentin and enamel. When dental technicians mill these restorations, the transitions between layers create a lifelike appearance.
3.2. Unique Features of Multilayer Zirconia
- Natural Aesthetics: Perfect for matching the patient’s natural teeth.
- Balanced Strength: Durable enough for most applications while prioritizing appearance.
- Versatility: Suitable for both anterior and posterior restorations.
4. Key Differences Between Monolithic and Multilayer Zirconia
4.1. Aesthetic Appearance
- Monolithic Zirconia: Opaque and utilitarian; best for posterior restorations.
- Multilayer Zirconia: Translucent with natural shading; ideal for anterior restorations.
4.2. Durability and Strength
- Monolithic Zirconia: The strongest option, ideal for bruxism patients or large-span bridges.
- Multilayer Zirconia: Strong enough for most cases but optimized for aesthetics.
4.3. Application in Crowns and Bridges
- Monolithic Zirconia: Focused on functionality and durability.
- Multilayer Zirconia: Chosen for cases where appearance is critical.
5. Clinical Scenarios for Choosing Between the Two
5.1. Restorative Requirements
Evaluate the location and functional needs of the restoration. For molars, monolithic zirconia offers strength; for front teeth, multilayer zirconia provides superior aesthetics.
5.2. Patient Preferences
Patients seeking natural-looking restorations may prefer multilayer zirconia, while those prioritizing durability might lean toward monolithic options.
6. Cost Considerations
The cost of materials plays a significant role in decision-making. Here’s how they compare:
6.1. Comparing the Price of Monolithic and Multilayer Zirconia
Monolithic Zirconia: More cost-effective, especially for posterior restorations.
Multilayer Zirconia: Higher material costs, offset by superior aesthetic results.
6.2. Balancing Cost and Value for Patients
When deciding between these options, consider the long-term value each material offers. Outsourcing to a reliable dental lab specializing in crowns and bridges can help control costs without sacrificing quality.
7. Which Zirconia is Best for Your Practice?
Choosing between Monolithic Zirconia and Esthetic Multilayer Zirconia depends on clinical needs, patient preferences, and cost considerations. By partnering with a dedicated dental lab outsourcing provider, dental organizations can offer customized solutions that balance aesthetics and functionality. Whether strength or beauty is your priority, zirconia restorations ensure optimal outcomes for crowns and bridges.
If you’re looking to optimize your lab’s output, consider partnering with a specialized outsourcing provider. Contact XDENT LAB today to explore how our services can help you deliver exceptional results for crowns and bridges, all while managing costs effectively.