Orthodontic treatments have advanced significantly in the past century, largely due to innovations in materials science. The evolution of orthodontic materials has enabled clinicians to achieve precise tooth movement, improved patient comfort, and enhanced aesthetic outcomes.
Table of contents [Show]
- Overview of Orthodontic Materials
- Main Categories of Orthodontic Materials
- Mechanical Properties and Clinical Significance
- Recent Innovations in Orthodontic Materials
- Clinical Applications and Treatment Considerations
- Biological Considerations and Biocompatibility
- Future Directions and Emerging Technologies
- Conclusion
Orthodontic treatments have advanced significantly in the past century, largely due to innovations in materials science. The evolution of orthodontic materials has enabled clinicians to achieve precise tooth movement, improved patient comfort, and enhanced aesthetic outcomes. Modern orthodontics relies on a diverse range of materials, each designed with specific mechanical, biological, and aesthetic properties to optimize treatment effectiveness.
This article provides an in-depth review of orthodontic materials, including their properties, applications, recent innovations, and future directions in orthodontic treatment.

Overview of Orthodontic Materials
Orthodontic materials are integral to the success of treatment, serving both functional and aesthetic purposes. The development of these materials has focused on enhancing mechanical performance, biocompatibility, and patient satisfaction. Common orthodontic materials include:
Wires: Essential for delivering controlled forces to teeth.
Brackets: Anchoring systems for wires, available in a variety of materials.
Elastics and auxiliaries: Additional components to aid tooth movement.
The selection of materials depends on their mechanical properties, clinical applications, and patient-specific factors, such as age, oral health, and aesthetic preferences.
Main Categories of Orthodontic Materials
Orthodontic Wires
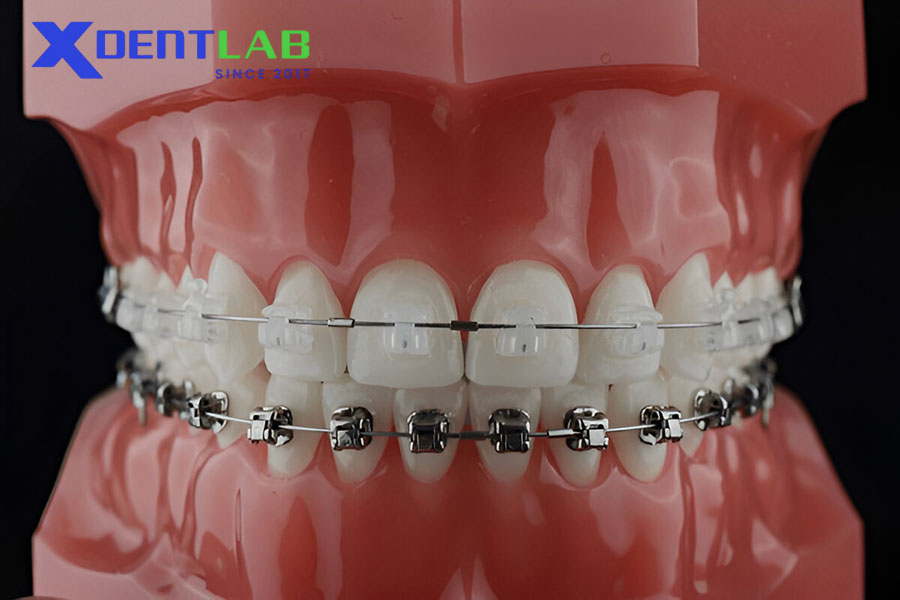
Orthodontic wires are the backbone of fixed appliance therapy, providing the forces necessary for tooth movement. Key wire materials include:
Stainless Steel Wires
Known for strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
Cost-effective and easy to manipulate.
Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) Wires
Revolutionary materials offering superelasticity and shape memory.
Ideal for initial alignment and leveling stages due to their light continuous forces.
Beta-Titanium Wires
Intermediate properties between stainless steel and NiTi.
Suitable for finishing and detailing stages, offering precise adjustments with lower force delivery.
Cobalt-Chromium Wires
High-strength alternatives with excellent corrosion resistance.
Useful for complex cases requiring greater rigidity.
Bracket Materials
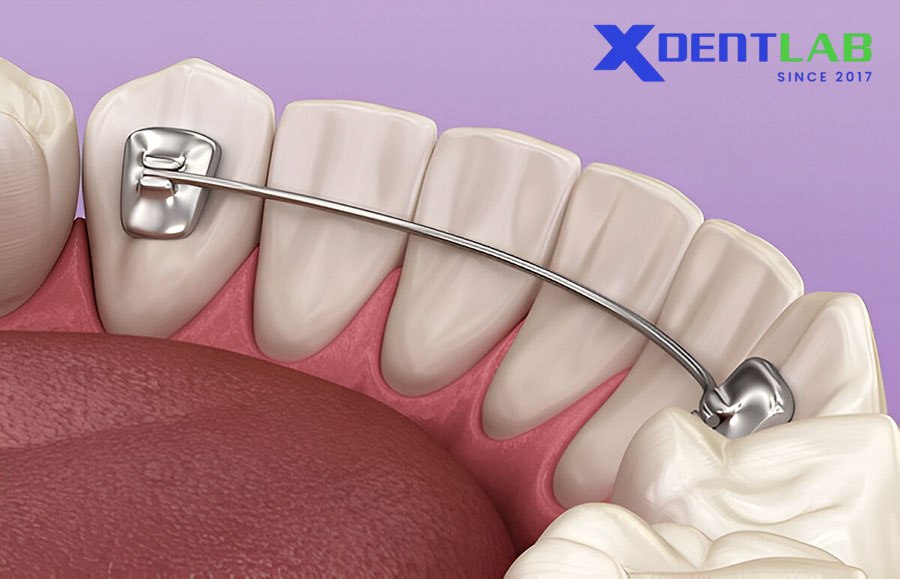
Orthodontic brackets serve as anchors for wires and play a crucial role in treatment mechanics and aesthetics. Common bracket materials include:
Predominantly stainless steel, offering durability and precision.
Widely used due to their mechanical reliability.
Ceramic Brackets
Aesthetic alternatives with improved translucency for less visible treatment.
Ideal for patients seeking discreet orthodontic solutions.
Polymer/Composite Brackets
Lightweight options with customizable mechanical properties.
Increasingly popular for aesthetic and functional versatility.
Self-Ligating Brackets
Advanced systems that reduce friction and treatment time.
Improve efficiency and patient comfort.
Mechanical Properties and Clinical Significance
Essential Mechanical Properties
Orthodontic materials are selected based on their mechanical characteristics, which directly impact treatment outcomes. Key properties include:
Elastic Modulus: Determines the stiffness and force delivery of wires and brackets.
Yield Strength: Indicates the stress level before permanent deformation occurs.
Springback: Reflects the ability of wires to return to their original shape after deformation.
Formability: Ease of bending and shaping materials for clinical customization.
Material-Specific Advantages
Each material category offers unique benefits in orthodontic treatment:
Stainless Steel: High strength, excellent formability, and cost-effectiveness.
Nickel-Titanium: Consistent light forces, superelasticity, and reduced patient discomfort.
Beta-Titanium: Balanced properties for precise adjustments during finishing stages.
Ceramic and Composite Brackets: Meeting patient demands for less visible appliances.
Recent Innovations in Orthodontic Materials
Bioactive Orthodontic Materials
The emergence of bioactive orthodontic materials has revolutionized treatment by integrating therapeutic functions. Innovations include:
Antimicrobial Coatings: Reduce bacterial adhesion, preventing white spot lesions.
Fluoride-Releasing Materials: Provide continuous caries protection during treatment.
Smart Materials: Responsive to environmental stimuli, optimizing treatment forces.
Biocompatible Surface Modifications: Enhance tissue response and reduce inflammation.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
Modern manufacturing processes have significantly improved orthodontic materials:
CAD/CAM Technology: Enables customized bracket and wire fabrication for patient-specific needs.
3D Printing: Allows for precise production of aligners and other appliances.
Nanotechnology: Creates molecular-level surface modifications for improved performance.
Heat Treatment Advances: Optimizes mechanical properties of alloys for better clinical outcomes.
Clinical Applications and Treatment Considerations
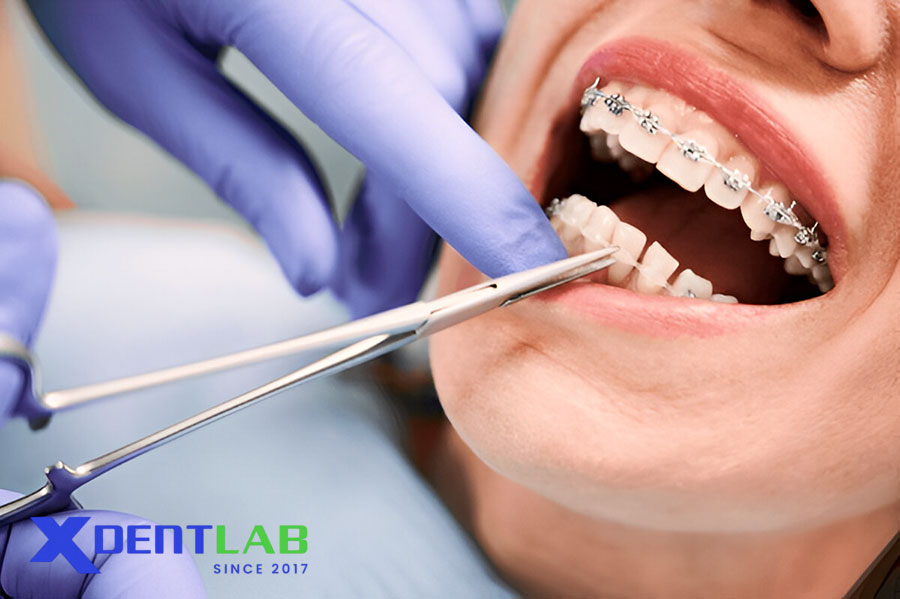
Material Selection Criteria
Selecting appropriate orthodontic materials requires consideration of several factors:
Treatment Stage: Initial alignment requires light, flexible materials, while finishing stages demand more rigid options.
Patient Age: Growing patients benefit from lighter and more biocompatible materials.
Aesthetic Demands: Balancing visibility with mechanical performance for adult patients.
Oral Environment: Materials must resist corrosion and maintain biocompatibility.
Evidence-Based Clinical Applications
Research highlights specific advantages for different materials:
Initial Alignment: NiTi wires provide optimal light continuous forces for early tooth movement.
Space Closure: Stainless steel wires offer rigidity and control for precise movement.
Finishing and Detailing: Beta-titanium wires allow for fine adjustments and detailing.
Retention: Thermoplastic materials improve patient compliance with retainers.
Biological Considerations and Biocompatibility
Tissue Response
Orthodontic materials must demonstrate excellent biocompatibility to ensure patient safety. Key considerations include:
Minimal Cytotoxicity: Materials must avoid adverse effects on oral tissues.
Corrosion Resistance: Prevent ion release into the oral environment.
Hypoallergenic Options: Alternatives for nickel-sensitive patients.
Tissue-Friendly Surfaces: Reduce plaque accumulation and inflammation.
Long-Term Biological Effects
Recent studies have investigated the biological impact of orthodontic materials:
Ion Release Studies: Monitor metal ion levels in saliva and tissues.
Cellular Response: Evaluate material effects on oral tissues and bone.
Microbiome Interactions: Assess material influence on oral bacteria and plaque formation.
Systemic Effects: Explore potential impacts on overall health.
Future Directions and Emerging Technologies
Smart Orthodontic Materials
The future of orthodontic materials lies in intelligent systems, including:
Shape Memory Polymers: Temperature-activated appliances for dynamic treatment.
Self-Healing Materials: Extend appliance longevity and reduce maintenance.
Programmable Force Delivery: Customized mechanics for optimized treatment.
Integrated Sensors: Real-time monitoring of treatment progress.
Sustainable Materials
Environmental considerations are driving the development of eco-friendly orthodontic materials:
Biodegradable Polymers: Reduce environmental impact of disposable components.
Recyclable Alloys: Promote sustainable lifecycle management.
Bio-Based Composites: Utilize natural fibers for reinforcement.
Reduced Waste Manufacturing: Improve efficiency in production processes.
Conclusion
Orthodontic materials are at the forefront of innovation, enabling clinicians to deliver precise, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing treatments. The integration of bioactive properties, advanced manufacturing techniques, and sustainable practices represents the future of orthodontic material science.
At XDENT LAB, we specialize in delivering high-quality orthodontic solutions that meet FDA and ISO standards. Our commitment to cutting-edge materials and technologies ensures dental practices achieve consistent and reliable results for their patients.
XDENT LAB is an expert in Lab-to-Lab Full Service from Vietnam, with the signature services of Removable & Implant, meeting U.S. market standards – approved by FDA & ISO. Founded in 2017, XDENT LAB has grown from local root to global reach, scaling with 2 factories and over 100 employees.. Our state-of-the-art technology, certified technicians, and commitment to compliance make us the trusted choice for dental practices looking to ensure quality and consistency in their products.
Our commitments are:
100% FDA-Approved Materials.
Large-Scale Manufacturing, high volume, remake rate < 1%.
2~3 days in lab (*digital file).
Your cost savings 30%.
Uninterrupted Manufacturing 365 days a year.
Contact us today to establish a strategy to reduce operating costs.
--------❃--------
Vietnam Dental Laboratory - XDENT LAB
🏢 Factory 1: 95/6 Tran Van Kieu Street, Binh Phu Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
🏢 Factory 2: Kizuna 3 Industrial Park, Can Giuoc Commune, Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam
☎ Hotline: 0919 796 718 📰 Get detailed pricing
Share this post: