Discover the comprehensive overview of stainless steel orthodontic brackets, including their composition, manufacturing processes, mechanical properties, surface modifications, corrosion resistance, and clinical performance. Learn why stainless steel brackets remain the gold standard in orthodontics.
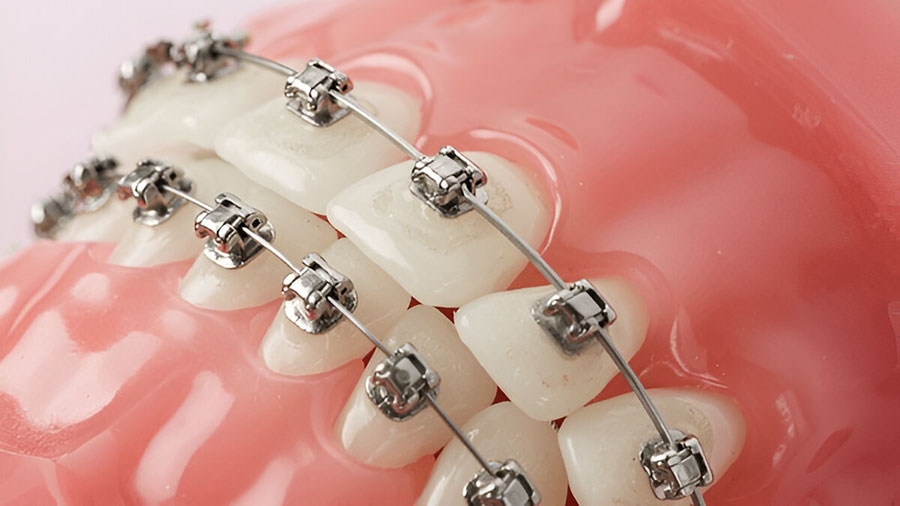
Table of contents [Show]
Stainless steel brackets are the backbone of modern orthodontics, offering unmatched mechanical strength, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. This article provides an in-depth look at their composition, manufacturing processes, clinical performance, and recent innovations, helping dental professionals make informed decisions about their use.
Stainless Steel Types Used
Stainless steel brackets are primarily made from austenitic grades:
316L (Surgical Grade): High corrosion resistance (16-18% Chromium, 10-14% Nickel, 2-3% Molybdenum).
304: Durable and corrosion-resistant (18-20% Chromium, 8-10.5% Nickel).
303: Added sulfur for improved machinability.
Key Benefits
Corrosion Resistance: Chromium forms a passive oxide layer.
Nickel: Enhances ductility and corrosion resistance.
Molybdenum (316L): Protects against pitting in chloride-rich environments.
Manufacturing Processes

Produces precise, complex geometries with uniform properties.
Cost-effective for mass production.
Milling/Machining
Offers superior dimensional accuracy.
Ideal for premium, high-quality brackets.
Investment Casting
Traditional method for intricate designs.
Requires additional finishing.
Sintering
Powder metallurgy technique for controlled porosity and good mechanical properties.
Mechanical Properties
Strength and Durability
Tensile Strength: 515-620 MPa.
Yield Strength: 205-310 MPa.
Hardness: 150-200 HV.
Elastic Modulus: 193-200 GPa.
Clinical Performance
High resistance to deformation and fatigue.
Low friction coefficient with stainless steel wires.
Maintains stability throughout treatment.
Surface Characteristics and Modifications
Base Surface Properties
Passive oxide layer ensures corrosion protection.
Surface roughness ranges from 0.2-0.8 μm.
Modern Modifications
Titanium Oxide Coating: Reduces bacterial adhesion and improves hygiene.
Laser-Structured Bases: Enhances mechanical retention and reduces enamel damage.
Ion Implantation: Adds antimicrobial and hardness properties.
Corrosion Behavior
Resistance Mechanisms
Self-healing chromium oxide film protects against corrosion.
Effective in oral environments (pH 4-9).
Types of Corrosion
Pitting: Localized damage in chloride-rich saliva.
Crevice: At bracket-adhesive interfaces, minimized by design.
Galvanic: Minimal when paired with similar metals.
Clinical Performance Data
Bond Strength
Shear bond strength: 8-15 MPa.
Tensile bond strength: 6-12 MPa.
Failure Rates
Clinical failure rate: 2-5% over 24 months.
Failure primarily occurs at the adhesive-enamel interface.
Precision
Slot tolerance: ±0.0005-0.002 inches.
Torque accuracy: 70-85% of prescribed values.
Biocompatibility Considerations
Nickel Release
Initial release: 0.2-0.5 μg/cm²/week.
Steady-state release: <0.1 μg/cm²/week.
Safe for most patients; 316L shows lower nickel release.
Cytotoxicity
ISO 10993 testing confirms no significant cytotoxic effects.
Minimal inflammatory response in tissues.
Advantages and Limitations

Key Advantages
High mechanical strength and durability.
Cost-effective and reliable.
Easy debonding with minimal enamel damage.
Suitable for all malocclusion types.
Limitations
Metallic appearance may not appeal to aesthetic-conscious patients.
Nickel sensitivity contraindicates use in some individuals.
MRI artifacts and potential discoloration in poor oral hygiene cases.
Recent Innovations
3D Printing: Customized bracket production for enhanced fit.
Smart Brackets: Force sensors and temperature-responsive elements for improved treatment control.
Antimicrobial Coatings: Sustained-release coatings for better hygiene.
Clinical Guidelines

Patient Selection
Ideal for adolescents and complex treatments.
Best for patients with good oral hygiene compliance.
Alternative materials recommended for nickel-sensitive patients.
Best Practices
Store properly to maintain surface integrity.
Use compatible adhesives and monitor for wear.
Educate patients on cleaning around brackets.
Conclusion
Stainless steel brackets remain the gold standard in orthodontics, offering unmatched strength, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. With ongoing innovations addressing their aesthetic and functional limitations, these brackets continue to set the benchmark for orthodontic treatment success.
XDENT LAB is an expert in Lab-to-Lab Full Service from Vietnam, with the signature services of Removable & Implant, meeting U.S. market standards – approved by FDA & ISO. Founded in 2017, XDENT LAB has grown from local root to global reach, scaling with 2 factories and over 100 employees.. Our state-of-the-art technology, certified technicians, and commitment to compliance make us the trusted choice for dental practices looking to ensure quality and consistency in their products.
Our commitments are:
100% FDA-Approved Materials.
Large-Scale Manufacturing, high volume, remake rate < 1%.
2~3 days in lab (*digital file).
Your cost savings 30%.
Uninterrupted Manufacturing 365 days a year.
Contact us today to establish a strategy to reduce operating costs.
--------❃--------
Vietnam Dental Laboratory - XDENT LAB
🏢 Factory 1: 95/6 Tran Van Kieu Street, Binh Phu Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
🏢 Factory 2: Kizuna 3 Industrial Park, Can Giuoc Commune, Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam
☎ Hotline: 0919 796 718 📰 Get detailed pricing
Share this post: