Precious metal alloys have been a cornerstone in modern dentistry, particularly in metal-based frameworks. Their exceptional properties, biocompatibility, and clinical performance make them an enduring choice for dental practices worldwide.
Table of contents [Show]
Precious metal alloys have been a cornerstone in modern dentistry, particularly in metal-based frameworks. Their exceptional properties, biocompatibility, and clinical performance make them an enduring choice for dental practices worldwide. This article explores the classification, composition, properties, and applications of precious metal alloys in dentistry, offering insights into why they remain vital in dental frameworks.

Classification and Composition
The American Dental Association (ADA) classifies precious metal alloys into three primary categories based on noble metal content:
High Noble Alloys
Composition: Must contain ≥60% noble metal content (gold and platinum group metals), with gold content ≥40%.
Examples: Au-Pt, Au-Pd, and Au-Pt-Pd alloys.
Applications: Ideal for crowns, bridges, and implant components due to their superior properties and biocompatibility.
Noble Alloys
Composition: Contain ≥25% noble metal content without specific requirements for gold content.
Examples: Pd-Ag, Pd-Cu, and Pd-Co alloys.
Applications: Widely used in fixed and removable prosthodontics as a cost-effective alternative to high noble alloys.
Composition: Contain <25% noble metal content, not classified as precious metal alloys.
Applications: Used primarily in cost-sensitive cases but lack the superior properties of precious metal alloys.
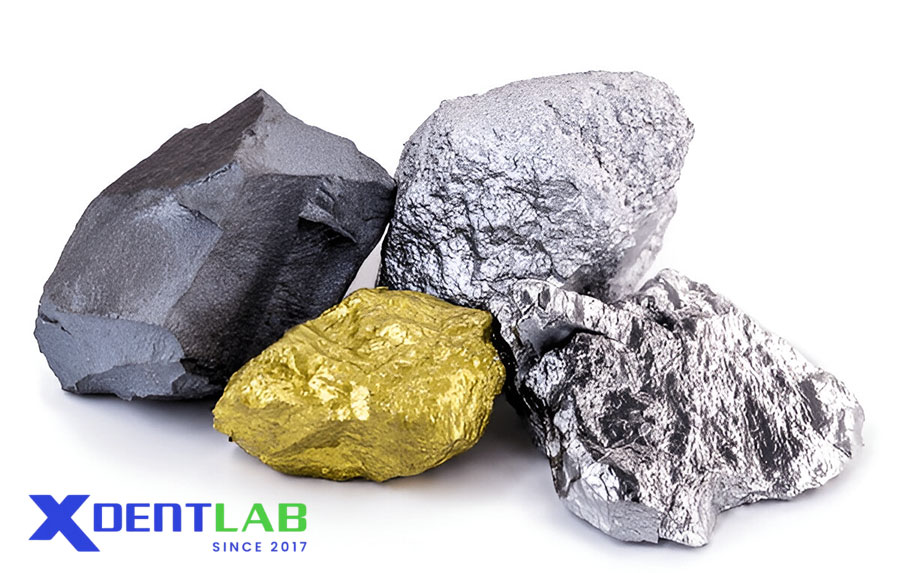

Noble metals are integral to dental alloys, offering unique properties that enhance performance:
Gold (Au): Primary component in high noble alloys; provides excellent ductility and biocompatibility.
Platinum (Pt): Increases strength and melting point, ensuring durability.
Palladium (Pd): A cost-effective alternative with corrosion resistance.
Iridium (Ir): Acts as a grain refiner for improved mechanical properties.
Ruthenium (Ru): Hardens alloys for better wear resistance.
Rhodium (Rh): Enhances alloy whiteness for aesthetic applications.
Osmium (Os): Rarely used due to limited availability.
Properties and Characteristics
Mechanical Properties
Elastic Modulus: Base metal alloys generally have higher elastic modulus compared to noble alloys, but high noble alloys provide better stress distribution.
Ductility and Malleability: Precious metals are highly adaptable, allowing precise fit and customization.
Chemical Properties
Corrosion Resistance: Noble metals form stable oxide layers, protecting against degradation.
Minimal Ion Release: Ensures a safe oral environment, particularly in Au-Pd alloys.
Biocompatibility
Tissue Compatibility: Precious metal alloys exhibit excellent soft tissue response and minimal allergic reactions.
Proven Track Record: Gold alloys have centuries of clinical success in dentistry.

Type I (Soft): Used in low-stress areas like inlays.
Type II (Medium): Suitable for inlays and onlays.
Type III (Hard): Designed for crowns and bridges.
Type IV (Extra Hard): Ideal for partial denture frameworks.
Au-Pt-Pd systems.
Au-Pd systems.
Pd-Ag systems.
High-palladium alloys.
Clinical Applications

Precious metal alloys are extensively used in various dental procedures:
Fixed Prosthodontics: Crowns, bridges, inlays, and onlays for durable and precise restorations.
Removable Prosthodontics: Partial denture frameworks offering strength and adaptability.
Implant Components: Abutments and superstructures ensuring biocompatibility and stability.
Metal-Ceramic Restorations: Strong frameworks with excellent aesthetic compatibility.
Clinical Benefits
Superior casting properties for precise reproduction of details.
Excellent marginal adaptation for long-term success.
Proven clinical track record with easy adjustability and polishing.
Biological Advantages
Minimal allergic potential and excellent soft tissue response.
No galvanic corrosion when properly used.
Technical Advantages
Lower melting temperatures for easier processing.
Excellent burnishability and soldering capabilities.
Disadvantages and Limitations
Economic Considerations
High cost due to precious metal content.
Price fluctuations in the metal market may impact affordability.
Aesthetic Limitations
Yellow color of gold alloys may show through thin ceramic layers.
Requires adequate ceramic thickness for optimal aesthetics.
Physical Properties
Lower elastic modulus compared to base metal alloys, requiring thicker sections for rigidity.
Softer than base metal alternatives, which may impact durability.
Composition Examples
High Noble Gold Alloys
Gold: 40-80%.
Platinum: 0-12%.
Palladium: 0-20%.
Silver: 0-15%.
Copper: 0-15%.
Noble Palladium Alloys
Palladium: 25-80%.
Silver: 0-40%.
Gold: 0-10%.
Copper: 0-15%.
Manufacturing and Processing
Casting Techniques
Lost-Wax Casting: Standard method for precision frameworks.
Modern Techniques: CAD/CAM milling, selective laser melting, and electroforming for advanced restorations.
Current Trends
Market Developments
Increased use of palladium-based systems due to cost-efficiency.
Integration with digital workflows for enhanced precision and efficiency.
Clinical Considerations
Precious metal alloys remain the gold standard for biocompatibility and long-span bridges requiring optimal stress distribution.
Conclusion
Precious metal alloys continue to play a vital role in dentistry, offering unmatched biocompatibility, proven clinical success, and superior working properties. Despite their higher cost, their advantages in fixed and removable prosthodontics, implant components, and metal-ceramic restorations make them indispensable for dental practices aiming to deliver quality and consistency.
At XDENT LAB, we specialize in crafting frameworks using precious metal alloys, ensuring compliance with FDA and ISO standards. With our state-of-the-art technology and expert technicians, we are committed to helping dental practices achieve excellence in patient care.
For trusted lab-to-lab service and premium dental solutions, contact XDENT LAB today!
XDENT LAB is an expert in Lab-to-Lab Full Service from Vietnam, with the signature services of Removable & Implant, meeting U.S. market standards – approved by FDA & ISO. Founded in 2017, XDENT LAB has grown from local root to global reach, scaling with 2 factories and over 100 employees.. Our state-of-the-art technology, certified technicians, and commitment to compliance make us the trusted choice for dental practices looking to ensure quality and consistency in their products.
Our commitments are:
100% FDA-Approved Materials.
Large-Scale Manufacturing, high volume, remake rate < 1%.
2~3 days in lab (*digital file).
Your cost savings 30%.
Uninterrupted Manufacturing 365 days a year.
Contact us today to establish a strategy to reduce operating costs.
--------❃--------
Vietnam Dental Laboratory - XDENT LAB
🏢 Factory 1: 95/6 Tran Van Kieu Street, Binh Phu Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
🏢 Factory 2: Kizuna 3 Industrial Park, Can Giuoc Commune, Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam
☎ Hotline: 0919 796 718 📰 Get detailed pricing
Share this post: