Stainless steel wires have been a cornerstone of orthodontic treatment since their introduction in the 1930s, replacing gold alloys as the primary material for orthodontic archwires. Their excellent mechanical properties, cost-effectiveness, and clinical reliability have made them one of the most widely used materials in orthodontics.
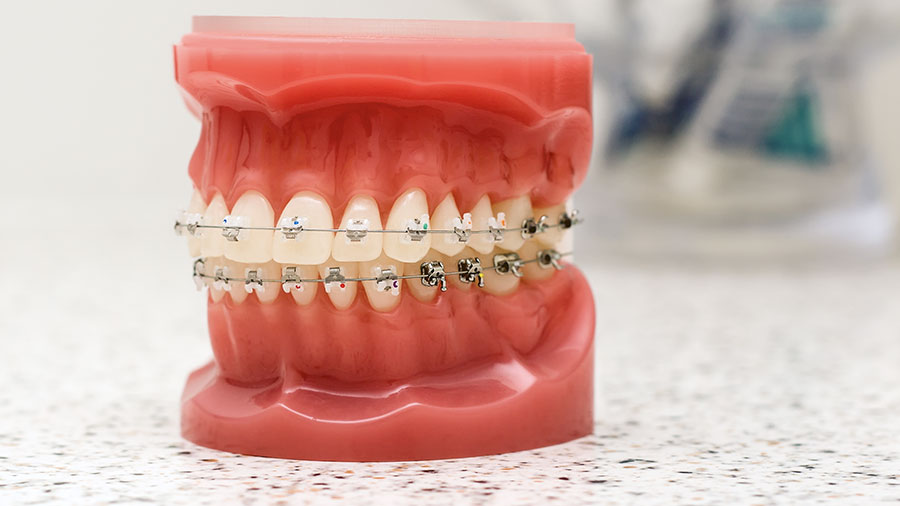
Table of contents [Show]
Stainless steel wires have been a cornerstone of orthodontic treatment since their introduction in the 1930s, replacing gold alloys as the primary material for orthodontic archwires. Their excellent mechanical properties, cost-effectiveness, and clinical reliability have made them one of the most widely used materials in orthodontics. Despite the emergence of advanced alternatives like nickel-titanium (NiTi) and beta-titanium wires, stainless steel remains indispensable in many treatment phases due to its predictable performance and long-standing track record.

This academic review explores the composition, mechanical properties, clinical applications, corrosion behavior, and recent advancements in stainless steel orthodontic wires, offering valuable insights for dental professionals.
Chemical Composition
Orthodontic stainless steel wires are predominantly made from austenitic AISI (American Iron and Steel Institute) 304 stainless steel alloy. The chemical composition includes:
Iron (Fe): Base element
Chromium (Cr): 17-20% (provides corrosion resistance through passive oxide layer formation)
Nickel (Ni): 8-12% (stabilizes the austenitic structure and enhances ductility)
Carbon (C): <0.08% (minimizes brittleness and maintains strength)
Minor Elements: Manganese, Silicon, and traces of other elements
Role of Chromium and Nickel
Chromium creates a protective oxide layer that prevents corrosion, while nickel enhances the ductility and toughness of the material, ensuring its suitability for orthodontic applications.
Microstructural Characteristics
Stainless steel wires exhibit an austenitic microstructure characterized by:
Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) Crystal Structure: Provides excellent formability and non-magnetic properties.
Corrosion Resistance: Effective in the oral environment due to the passive oxide layer.
Dimensional Stability: Ensures predictable performance during treatment.
Mechanical Properties

Physical and Mechanical Characteristics
Stainless steel wires are known for their superior mechanical properties:
Strength Properties
Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS): High, ensuring durability under stress.
Yield Strength (YS): Prevents permanent deformation during activation.
Modulus of Elasticity: Approximately 200 GPa, providing high stiffness and predictable force delivery.
Surface Characteristics
Smooth Surface: Reduces friction during sliding mechanics.
Low Spring-Back: Ensures accurate tooth movement and torque control.
Comparative Analysis
When compared to other orthodontic wire materials:
Higher Stiffness: Ideal for precise control in later treatment stages.
Superior Formability: Allows for intricate adjustments and loop mechanics.
Predictable Force Delivery: Ensures consistent clinical results.
Clinical Applications
Treatment Stages
Stainless steel wires are particularly effective in the following orthodontic treatment phases:
Working/Intermediate Stage
Space closure with sliding mechanics.
Torque expression for controlled tooth movement.
Finishing and Detailing Stage
Precise tooth positioning.
Final occlusal adjustments and arch coordination.
Wire Dimensions and Applications
Orthodontists often select wire dimensions based on treatment goals:
0.016″ × 0.022″: For initial working mechanics.
0.017″ × 0.025″: Suitable for heavier forces and space closure.
0.019″ × 0.025″: Maximum control and torque expression during finishing stages.
Loop Mechanics
Studies on loop designs (6mm, 8mm, 10mm heights) in stainless steel wires demonstrate variations in force delivery, enabling clinicians to tailor treatment based on specific patient needs.
Corrosion Behavior
Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel wires exhibit excellent corrosion resistance due to the formation of a passive oxide layer. This layer protects against:
Pitting Corrosion: Common in the oral environment.
Ion Release: Minimal under normal conditions, ensuring patient safety.
Comparative Corrosion Studies
Research comparing stainless steel to NiTi wires in simulated saliva environments shows:
Lower Nickel Ion Release: Reducing allergenic risks.
Stable Performance: Across varying pH levels and oral conditions.
Surface Modifications and Coatings

Zinc-Coated Stainless Steel Wires
Recent advancements include zinc-coated stainless steel wires, which offer:
Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal: Improved visual properties for patients concerned about metallic appearance.
Antimicrobial Benefits: Potential reduction in bacterial adhesion.
Maintained Mechanical Integrity: Ensures clinical performance remains unchanged.
Coating Process
The zinc coating is applied using physical vapor deposition (PVD) techniques, ensuring uniform thickness and preservation of underlying wire properties.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
Mechanical Properties
High strength and stiffness for controlled tooth movement.
Excellent formability for intricate adjustments.
Clinical Benefits
Cost-effective compared to advanced materials.
Long-standing clinical reliability and versatility.
Biocompatibility
Generally well-tolerated with minimal allergenic potential.
Stable performance in the oral environment.
Limitations
Aesthetic Concerns
Metallic appearance may be undesirable for some patients.
Force Characteristics
High stiffness may deliver excessive forces if improperly selected.
Friction
While lower than other materials, friction during sliding mechanics can affect efficiency.
Recent Developments and Research
Current Research Trends
Recent bibliometric studies highlight advancements in:
Surface Modifications: Nanostructured coatings for reduced friction.
Aesthetic Enhancements: Coatings to improve patient satisfaction.
Biocompatibility Studies: Addressing nickel-related concerns.
Future Directions
Emerging innovations include:
Smart Wire Technologies: Responsive materials for dynamic force delivery.
Antimicrobial Coatings: Reducing bacterial adhesion and oral infections.
Improved Manufacturing Processes: Enhancing consistency and reducing costs.
Clinical Recommendations
Wire Selection Guidelines
For optimal results, clinicians should:
Use larger dimensions (e.g., 0.019″ × 0.025″) for torque control.
Select intermediate sizes for space closure and sliding mechanics.
Combine stainless steel wires with appropriate bracket systems for efficiency.
Best Practices
To maximize performance:
Regularly monitor force levels during treatment.
Tailor wire selection to patient-specific needs.
Ensure proper activation protocols to avoid excessive forces.
Conclusion
Stainless steel wires remain an essential material in orthodontics due to their exceptional mechanical properties, clinical versatility, and cost-effectiveness. While newer materials like NiTi and beta-titanium offer advantages in specific applications, stainless steel continues to play a pivotal role in intermediate and finishing stages of treatment.
With ongoing research into surface modifications, aesthetic enhancements, and antimicrobial coatings, stainless steel wires are poised to maintain their relevance in modern orthodontics. For dental practices seeking reliable orthodontic materials, XDENT LAB provides high-quality stainless steel wires manufactured to FDA and ISO standards, ensuring consistent performance and patient satisfaction.
XDENT LAB is an expert in Lab-to-Lab Full Service from Vietnam, with the signature services of Removable & Implant, meeting U.S. market standards – approved by FDA & ISO. Founded in 2017, XDENT LAB has grown from local root to global reach, scaling with 2 factories and over 100 employees.. Our state-of-the-art technology, certified technicians, and commitment to compliance make us the trusted choice for dental practices looking to ensure quality and consistency in their products.
Our commitments are:
100% FDA-Approved Materials.
Large-Scale Manufacturing, high volume, remake rate < 1%.
2~3 days in lab (*digital file).
Your cost savings 30%.
Uninterrupted Manufacturing 365 days a year.
Contact us today to establish a strategy to reduce operating costs.
--------❃--------
Vietnam Dental Laboratory - XDENT LAB
🏢 Factory 1: 95/6 Tran Van Kieu Street, Binh Phu Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
🏢 Factory 2: Kizuna 3 Industrial Park, Can Giuoc Commune, Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam
☎ Hotline: 0919 796 718 📰 Get detailed pricing
Share this post: