When it comes to removable denture dental lab work, precision is key to achieving comfort and functionality for patients. One of the most crucial aspects of denture fabrication is the shaping and adjustment of the floor of the mouth. This area plays a significant role in the fit, stability, and overall comfort of the dentures.
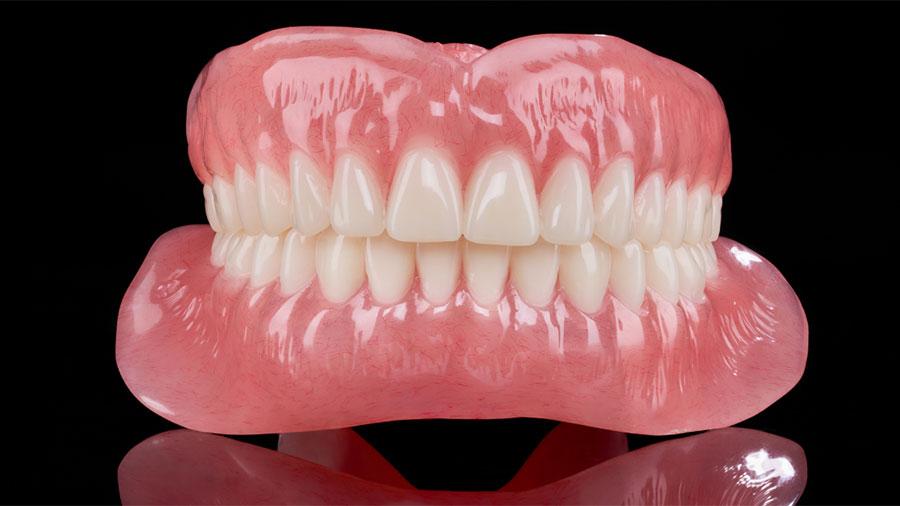
Table of contents [Show]
When it comes to removable denture dental lab work, precision is key to achieving comfort and functionality for patients. One of the most crucial aspects of denture fabrication is the shaping and adjustment of the floor of the mouth. This area plays a significant role in the fit, stability, and overall comfort of the dentures.

Understanding the Floor of the Mouth and Its Importance
The floor of the mouth is the area beneath the tongue, located inside the lower part of the oral cavity. This region is crucial for the fit of removable dentures because it helps anchor the denture in place, preventing it from shifting during eating or speaking. Additionally, proper shaping of the floor of the mouth ensures that the denture does not cause discomfort or irritation to the surrounding soft tissues. In removable denture dental lab processes, understanding the anatomy of the floor of the mouth is essential. The lab technicians must carefully design the denture base to fit the contours of this area, ensuring the dentures sit securely without affecting the patient’s comfort.
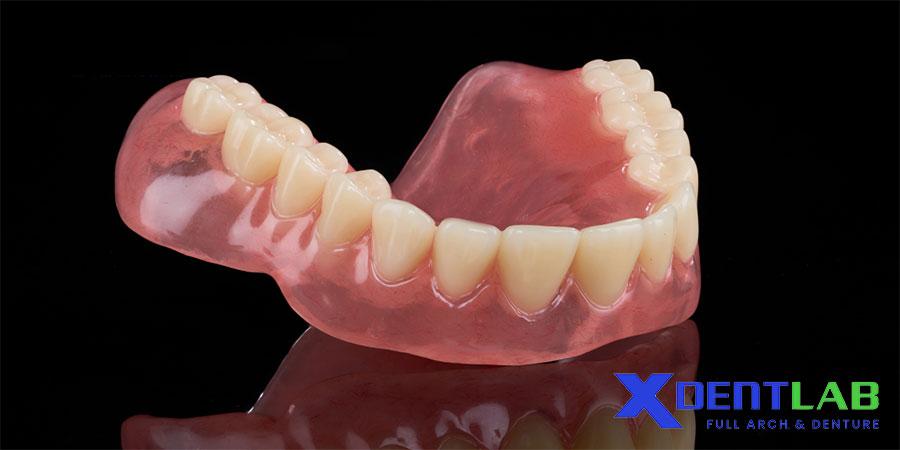
How Dental Labs Adjust the Floor of the Mouth in Removable Denture Fabrication
In a removable denture dental lab, creating dentures that fit comfortably and function effectively requires a deep understanding of the floor of the mouth's anatomy. Here’s how dental labs approach the shaping and adjustment process:
Precise Impressions
The first step in any denture fabrication process is taking accurate impressions of the patient’s mouth. This includes capturing the details of the floor of the mouth. The impression must be as detailed as possible to ensure that the denture base fits perfectly against this area. Special impression materials are used to capture the contours of the floor of the mouth, which helps create an accurate model for the denture.
Customizing the Denture Base
Once the impressions are taken, the dental lab technician creates a model of the patient’s mouth and begins to design the denture. The floor of the mouth must be carefully considered when creating the denture base. The lab technician may adjust the base’s shape to ensure it rests comfortably and securely on the floor of the mouth, avoiding any pressure on sensitive areas.
Testing the Fit
After the denture base is constructed, it is tested in the patient’s mouth to ensure a perfect fit. This stage allows the lab technician to make any necessary adjustments to the floor of the mouth area. If any discomfort or irritation occurs, the technician will refine the denture base to improve its fit.
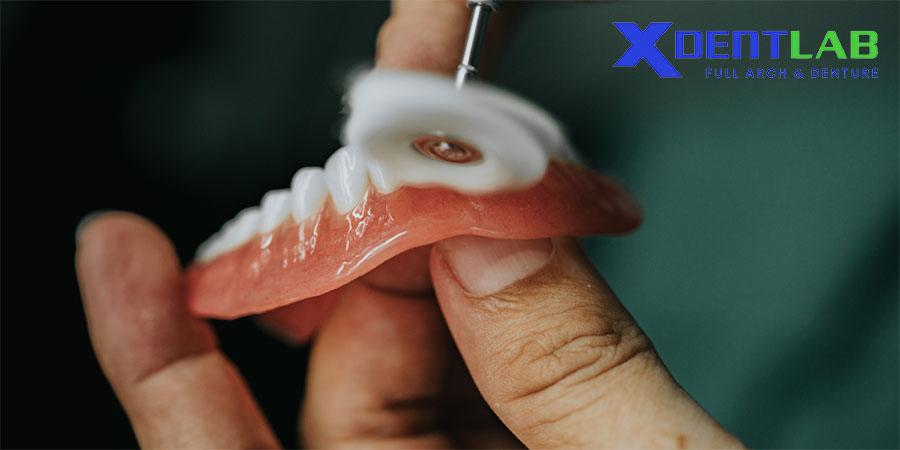
Final Adjustments and Polishing
The final step is polishing the denture and making any last-minute adjustments to the floor of the mouth region. This ensures that the denture is not only comfortable but also aesthetically pleasing and functional.
Conclusion
The correct shaping and adjustment of the floor of the mouth in removable denture dental lab fabrication is a vital aspect of creating dentures that are comfortable, stable, and natural-looking. By paying careful attention to this region, dental labs can ensure that their dentures fit well, provide a secure bite, and offer patients an improved quality of life. If you’re in need of high-quality removable dentures, choosing a skilled dental lab that prioritizes the correct shaping and adjustment of the floor of the mouth is essential for the best results.

At XDENT LAB, we have specialized in the production of removable dentures for the U.S. market since 2019. With extensive experience serving dental laboratory clients within the dental service organization (DSO) network, we adhere to stringent production and export standards, including ISO and FDA compliance. You can explore examples of our daily real-world cases here: https://xdentlab.com/xdent-gallery.
XDENT LAB is an expert in Lab-to-Lab Full Service from Vietnam, with the signature services of Removable & Implant, meeting U.S. market standards – approved by FDA & ISO. Founded in 2017, XDENT LAB has grown from local root to global reach, scaling with 2 factories and over 100 employees.. Our state-of-the-art technology, certified technicians, and commitment to compliance make us the trusted choice for dental practices looking to ensure quality and consistency in their products.
Our commitments are:
100% FDA-Approved Materials.
Large-Scale Manufacturing, high volume, remake rate < 1%.
2~3 days in lab (*digital file).
Your cost savings 30%.
Uninterrupted Manufacturing 365 days a year.
Contact us today to establish a strategy to reduce operating costs.
--------❃--------
Vietnam Dental Laboratory - XDENT LAB
🏢 Factory 1: 95/6 Tran Van Kieu Street, Binh Phu Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
🏢 Factory 2: Kizuna 3 Industrial Park, Can Giuoc Commune, Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam
☎ Hotline: 0919 796 718 📰 Get detailed pricing
Share this post:





