Glass ionomer cement (GIC) is a versatile dental material widely used in restorative dentistry due to its unique properties of chemical adhesion, fluoride release, and biocompatibility. It is particularly valued in minimally invasive dentistry and is suitable for a variety of clinical applications.

Table of contents [Show]
- Definition and Overview
- Chemical Composition
- Classification of Glass Ionomer Cements
- Setting Reaction Mechanism
- Properties of Glass Ionomer Cements
- Clinical Applications
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Glass Ionomer Cement
- Clinical Technique
- Commercial Products
- Recent Developments
- Clinical Research and Evidence
- Clinical Selection Guidelines
- Future Perspectives
- Conclusion
Glass ionomer cement (GIC) is a versatile dental material widely used in restorative dentistry due to its unique properties of chemical adhesion, fluoride release, and biocompatibility. It is particularly valued in minimally invasive dentistry and is suitable for a variety of clinical applications.

Definition and Overview
Glass ionomer cement is an acid-base material composed of a reaction between weak polymeric acids and powdered glasses of basic character. It is known for its ability to chemically bond to tooth structure and release fluoride, making it a preferred choice for direct restorative procedures.
Chemical Composition
Powder Component
Fluoro-aluminosilicate Glass
SiO₂ (Silicon dioxide): 29-50%.
Al₂O₃ (Aluminum oxide): 16-30%.
CaF₂ (Calcium fluoride): 15-35%.
Na₃AlF₆ (Cryolite): 5-10%.
AlF₃ (Aluminum fluoride): 5-10%.
AlPO₄ (Aluminum phosphate): 3-10%.
Liquid Component
Polyacrylic Acid: 45-50%.
Itaconic Acid: 5-10% (improves properties).
Tartaric Acid: 5-10% (controls setting time).
Water: 45-50%.
Classification of Glass Ionomer Cements
Based on Chemical Composition
Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement (CGIC): Pure acid-base reaction with a water-based system.
Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cement (RMGIC): Includes resin components like HEMA for improved mechanical properties and moisture control.
High-Viscosity Glass Ionomer Cement (HVGIC): Higher powder/liquid ratio for enhanced strength, used in Atraumatic Restorative Treatment (ART).
Based on Clinical Application
Type I - Luting Cements: For crown and bridge cementation with a thin film thickness.
Type II - Restorative Cements: For aesthetic and reinforced restorations, including primary teeth.
Type III - Lining/Base Cements: For cavity lining and pulp protection.
Based on Presentation Form
Powder-Liquid Systems: Traditional hand-mixed.
Encapsulated Systems: Mechanically mixed.
Paste-Paste Systems: Mainly RMGIC.
Setting Reaction Mechanism
Acid-Base Reaction
Decomposition Phase (0-4 minutes): H⁺ ions from polyacrylic acid attack the glass surface, releasing ions and forming an initial gel.
Hydrogel Phase (4-15 minutes): Formation of calcium polyacrylate and initial matrix.
Polysalt Phase (24 hours - 7 days): Formation of aluminum polyacrylate, increasing mechanical strength and chemical stabilization.
Setting Reaction Equation
Glass + Polyacrylic acid → Metal polyacrylate + Silica gel + F⁻.
Properties of Glass Ionomer Cements
Mechanical Properties
Conventional GIC: Compressive strength (150-200 MPa), tensile strength (4-6 MPa).
RMGIC: Enhanced compressive strength (180-250 MPa), tensile strength (10-15 MPa).
Biological Properties
Fluoride Release: High initial release with sustained low-level release and recharge capability.
Biocompatibility: Minimal pulp irritation with proper lining.
Physical-Chemical Properties
Solubility (0.4-1.5%), water absorption (1-3%), moderate wear resistance, and less translucency compared to composites.
Clinical Applications
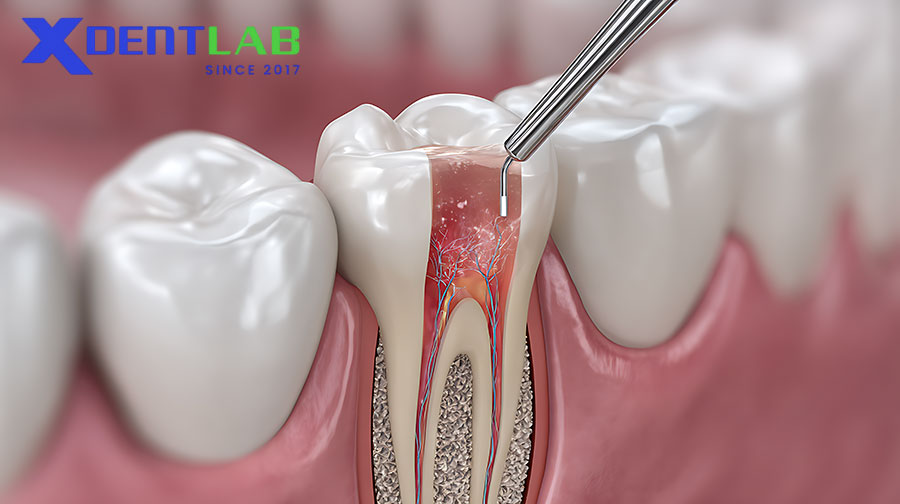
Restorative Applications
Ideal for Class III and V cavities, primary teeth restorations, core build-up, ART technique, and as a base under composites.
Luting Applications
Used for cementing metal crowns, bridges, inlays, onlays, orthodontic bands, and posts.
Preventive Applications
Effective for pit and fissure sealants, dentin hypersensitivity treatment, remineralization, and interim therapeutic restorations.
Lining/Base Applications
Used under amalgam and composite restorations for pulp-dentin complex protection.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Glass Ionomer Cement

Advantages of GIC
Chemical Adhesion
Bonds to calcium in hydroxyapatite without etching, minimizing microleakage.
Fluoride Release
Prevents secondary caries with antibacterial properties and promotes remineralization.
Biocompatibility
Safe for pediatric use with minimal pulp irritation and low cytotoxicity.
Clinical Convenience
Simple technique, less sensitive to technique, suitable for field conditions, and allows bulk placement.
Disadvantages and Limitations
Poor Mechanical Properties
Brittle with low fracture resistance, unsuitable for high occlusal forces.
Aesthetic Limitations
Poor translucency and limited shade range, difficult to polish.
Moisture Sensitivity
Susceptible to early dehydration and water contamination, requiring surface protection.
Setting Characteristics
Slow setting with full strength achieved after 24 hours, sensitive to temperature.
Clinical Technique
Cavity Preparation
Remove carious tissue, clean with polyacrylic acid, rinse gently, and avoid desiccation.
Material Mixing
Follow manufacturer's P/L ratio instructions, mix for 30-60 seconds using a folding motion to achieve a glossy consistency.
Material Placement
Work within 2-3 minutes, place incrementally for deep cavities, and avoid air incorporation.
Finishing Procedures
Conventional GIC requires finishing after 24 hours, while RMGIC allows immediate finishing. Apply protective varnish if needed.
Commercial Products
Conventional GIC
Fuji IX GP (GC Corporation), Ketac Molar (3M ESPE), ChemFil Rock (Dentsply Sirona).
RMGIC
Fuji II LC (GC Corporation), Photac Fil (3M ESPE), Vitremer (3M ESPE).
Luting GIC
Fuji I (GC Corporation), Ketac Cem (3M ESPE), Aqua Cem (Dentsply Sirona).
Recent Developments
Nano-GIC
Incorporation of nanoparticles for enhanced mechanical properties and polishability.
Bioactive GIC
Stimulates tissue regeneration and enhanced remineralization with bioactive glass and antimicrobial additives.
Smart GIC
Features pH-responsive behavior, controlled ion release, and self-healing properties.
Clinical Research and Evidence
Success Rates: High success in non-stress bearing restorations, primary teeth, ART restorations, and luting applications.
Failure Modes: Include material loss, bulk fracture, secondary caries, and loss of retention.
Longevity Factors: Depend on proper case selection, technique, material quality, and patient factors.
Clinical Selection Guidelines
Ideal Indications: Non-stress bearing cervical lesions, primary teeth restorations, high caries risk patients, and ART approach.
Contraindications: High stress-bearing areas, high aesthetic demands, bruxism, large cavities, and cusp replacement.
Future Perspectives
Research Directions: Focus on improving mechanical properties, aesthetics, setting mechanisms, and developing smart materials with regenerative capabilities.
Clinical Trends: Emphasize minimally invasive dentistry, bioactive restorations, preventive approaches, and sustainable materials.
Conclusion
Glass ionomer cements continue to be valuable materials in modern dentistry. Their chemical adhesion, fluoride release, and biocompatibility make them suitable for specific clinical situations. Understanding their properties, indications, and proper handling techniques is crucial for clinical success. As material science advances, newer formulations will expand the applications of GIC while addressing traditional limitations.
XDENT LAB is an expert in Lab-to-Lab Full Service from Vietnam, with the signature services of Removable & Implant, meeting U.S. market standards – approved by FDA & ISO. Founded in 2017, XDENT LAB has grown from local root to global reach, scaling with 2 factories and over 100 employees.. Our state-of-the-art technology, certified technicians, and commitment to compliance make us the trusted choice for dental practices looking to ensure quality and consistency in their products.
Our commitments are:
100% FDA-Approved Materials.
Large-Scale Manufacturing, high volume, remake rate < 1%.
2~3 days in lab (*digital file).
Your cost savings 30%.
Uninterrupted Manufacturing 365 days a year.
Contact us today to establish a strategy to reduce operating costs.
--------❃--------
Vietnam Dental Laboratory - XDENT LAB
🏢 Factory 1: 95/6 Tran Van Kieu Street, Binh Phu Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
🏢 Factory 2: Kizuna 3 Industrial Park, Can Giuoc Commune, Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam
☎ Hotline: 0919 796 718 📰 Get detailed pricing
Share this post: