Practical chairside playbook: risk assessment, moisture control, enameloplasty, thin‑layer placement, and documentation to standardize filled sealant success.
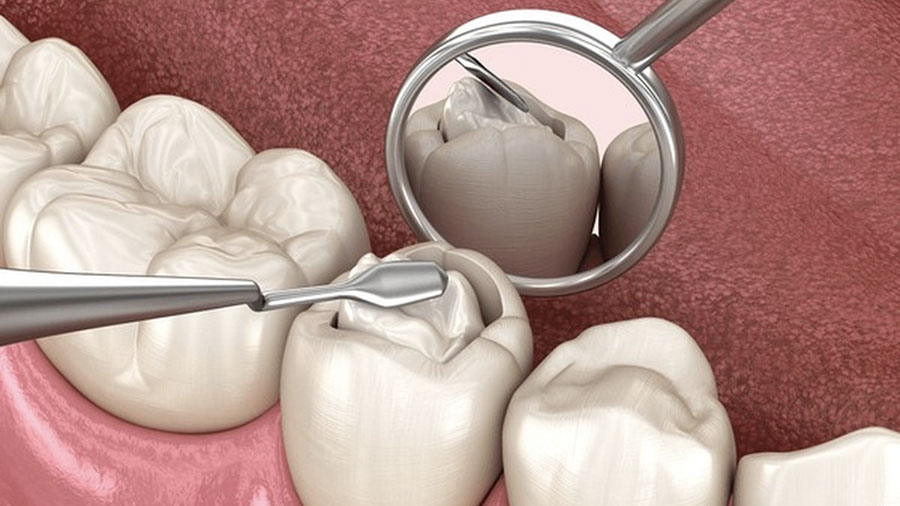
Table of contents [Show]
- Overview
- Definition & Composition
- Physical & Mechanical Properties
- Clinical Performance
- Clinical Applications
- Advantages & Disadvantages
- Disadvantages
- Recent Research Developments
- Technique & Workflow Recommendations
- Comparative Perspective: Filled vs. Unfilled
- Quality, Safety, and Compliance
- Economic Considerations
- XDENT LAB Perspective
Overview
Filled resin sealants are resin-based pit-and-fissure sealants enhanced with inorganic filler particles to improve strength, wear resistance, and radiographic detectability. While their higher viscosity can limit deep fissure penetration compared to unfilled sealants, filled formulations are valuable for long-term occlusal protection in high-risk patients and newly erupted molars—especially when applied under standardized isolation and conditioning protocols. Below is a clinical-science synthesis that balances material properties, retention evidence, and practical chairside considerations.
Definition & Composition
Filled resin sealants incorporate a reinforced matrix designed for durability and radiopacity.
What They’re Made Of
Resin matrix: typically BIS-GMA or related dimethacrylate monomers; some systems include urethane dimethacrylates.
Filler particles: inorganic fillers (e.g., silica, glass) with variable size/content for strength and radiopacity.
Coupling agents: silanes to bond fillers to the resin matrix.
Photoinitiators: light-activated systems to achieve polymerization under blue light.
Why Fillers Matter
Increase modulus and abrasion resistance.
Enable radiographic visualization and follow-up.
Influence viscosity, flow, and penetration into fissure anatomy.
Physical & Mechanical Properties
The clinical behavior of filled sealants reflects a trade-off between penetration and durability.
Viscosity & Penetration
Filled sealants: higher viscosity, potentially reduced flow into very narrow pits and fissures.
Unfilled sealants: lower viscosity, deeper penetration; may favor early retention in complex fissure anatomy.
Practical implication: meticulous enamel conditioning and isolation help offset penetration limits of filled systems.
Wear Resistance & Durability
Enhanced abrasion resistance under occlusal load.
Improved fracture resistance and marginal stability.
Radiopaque variants support maintenance decisions and re-seal strategy over time.
Clinical Performance
Evidence compares filled vs. unfilled sealants on retention, microleakage, and caries prevention.
Retention Rates
Meta-analytic findings indicate variable results: some trials show unfilled systems with slightly higher early retention, while long-term differences narrow with proper technique.
Determinants of success: tooth eruption stage, moisture control, etching protocol, operator consistency, and occlusal load patterns.
Microleakage
Both filled and unfilled formulations can perform well when enamel is properly etched and isolated.
Conditioning strategy (etch-only vs. etch-and-adhesive) and hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of the sealant influence microleakage outcomes.
Clinical Applications
Target indications prioritize caries risk and occlusal load considerations.
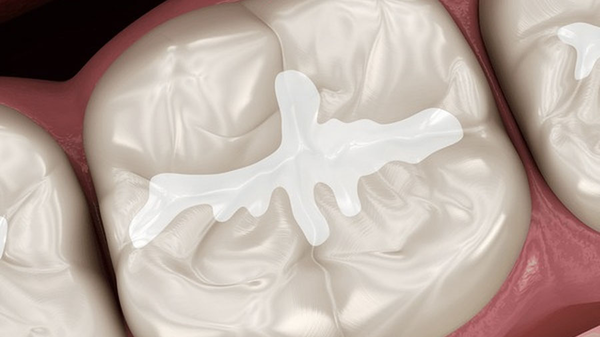
Caries Prevention
Physical barrier prevents plaque and food impaction in pits and fissures.
Most impactful in high-caries-risk populations and deep fissure anatomies.
Target Populations
Newly erupted permanent molars with immature enamel and challenging isolation.
High-caries-risk children and adolescents.
Patients needing durable, long-term occlusal protection where wear resistance is paramount.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Real-world trade-offs guide material selection and technique.
Advantages
Superior wear resistance under mastication.
Enhanced mechanical strength and marginal stability.
Radiopacity aiding follow-up and diagnostics.
Controlled handling due to higher viscosity (reduces overrun).
Disadvantages
Reduced penetration into extremely narrow fissures.
Potentially lower early retention in some studies without adhesive use.
Technique sensitivity: requires rigorous isolation and careful placement.
Recent Research Developments
Emerging formulations and protocols aim to reconcile penetration with durability.
Material & Formulation Trends
Hydrophilic filled sealants vs. hydrophobic counterparts: differential microshear bond strength, microleakage, and penetration depth under suboptimal moisture.
Nano/micro-hybrid fillers: attempts to balance flow and mechanical reinforcement.
Enamel Conditioning Insights
Etch-only vs. etch + adhesive systems: adhesives can improve wetting/penetration, potentially enhancing retention.
Selective enameloplasty: widening tight fissures to facilitate flow of filled sealants.
Long-Term Outcomes
Systematic reviews emphasize consistent caries prevention with both types when isolation and technique are standardized.
Re-seal protocols improve longevity and cost-effectiveness across multi-year follow-up.
Technique & Workflow Recommendations
A disciplined protocol maximizes clinical success with filled sealants.
Pre-Placement
Risk assessment: caries risk, fissure morphology, eruption status.
Isolation: rubber dam preferred; high-quality moisture control is non-negotiable.
Cleaning: pumice or non-oil prophylaxis; avoid fluoride/varnish immediately pre-placement.
Enamel Conditioning
35–37% phosphoric acid etch (20–30 seconds), thorough rinse, and dry to chalky enamel.
Consider dental adhesive (thin, air-dried, light-cured) to improve wettability in deep fissures.
Placement & Polymerization
Conservative enameloplasty if fissures are extremely narrow.
Thinned initial layer to promote penetration; avoid air entrapment.
Light cure per manufacturer; verify output and tip distance.
Verification & Maintenance
Check occlusion; remove excess; avoid high spots.
Document radiopaque presence; schedule review and re-seal as needed.
Comparative Perspective: Filled vs. Unfilled
Selection depends on anatomy, moisture control, and longevity goals.
When Filled Sealants Shine
High-load occlusal areas and patients with bruxism tendencies.
Situations prioritizing radiographic follow-up and long-term durability.
Clinics with excellent isolation protocols and adhesive-assisted placement.
When Unfilled Sealants Fit
Extremely narrow fissures or suboptimal isolation scenarios.
Early eruption stages with complex morphology.
Rapid application contexts emphasizing flow and initial retention.
Quality, Safety, and Compliance
Standardization safeguards outcomes and supports audit readiness.

QA Essentials
Light-curing verification (radiometer checks).
Batch and lot tracking; material certificates retained in device history records.
Operator calibration: periodic audits of retention and microleakage proxies.
Regulatory Alignment
Follow regional guidance for preventive sealants; maintain informed consent and documentation.
For U.S.-aligned workflows, adopt ISO 13485‑style record-keeping and validated process controls.
Economic Considerations
Sealants are high-impact, low-cost interventions—technique drives ROI.
Cost & Value
Material cost is modest; the real value lies in reduced caries incidence and restorative burden.
Re-seal maintenance pathways extend functional lifespan and minimize retreatment costs.
Practice Efficiency
Standardized kits and checklists shorten chairtime variability.
Radiopaque filled sealants streamline review appointments and decision-making.
XDENT LAB Perspective
As a Lab-to-Lab partner, XDENT LAB supports preventive programs with protocol education, material sourcing, and QA documentation aligned to FDA/ISO expectations. Our technicians assist with conditioning strategies, curing verification, and traceability, helping practices achieve consistent sealant outcomes in high-risk populations.
XDENT LAB is an expert in Lab-to-Lab Full Service from Vietnam, with the signature services of Removable & Implant, meeting U.S. market standards – approved by FDA & ISO. Founded in 2017, XDENT LAB has grown from local root to global reach, scaling with 2 factories and over 100 employees.. Our state-of-the-art technology, certified technicians, and commitment to compliance make us the trusted choice for dental practices looking to ensure quality and consistency in their products.
Our commitments are:
100% FDA-Approved Materials.
Large-Scale Manufacturing, high volume, remake rate < 1%.
2~3 days in lab (*digital file).
Your cost savings 30%.
Uninterrupted Manufacturing 365 days a year.
Contact us today to establish a strategy to reduce operating costs.
--------❃--------
Vietnam Dental Laboratory - XDENT LAB
🏢 Factory 1: 95/6 Tran Van Kieu Street, Binh Phu Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
🏢 Factory 2: Kizuna 3 Industrial Park, Can Giuoc Commune, Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam
☎ Hotline: 0919 796 718 📰 Get detailed pricing
Share this post: