Concise, practical guide to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Covers regulatory frameworks (21 CFR), quality systems, documentation, validation, inspections, data integrity (ALCOA+), and best practices—tailored for dental manufacturers and labs seeking consistent, compliant operations.

Table of contents [Show]
- Overview
- Introduction & Definition
- Core Principles of FDA GMP
- Regulatory Framework
- Key GMP Requirements
- Documentation Requirements
- Process Control & Validation
- Quality Control & Testing
- Compliance & Inspection
- Industry‑Specific GMPs
- Data Integrity in GMP
- Risk Management in GMP
- Training & Competency
- Supplier Management
- Continuous Improvement
- Global Harmonization
- Future of GMP
- Implementation Best Practices
- Conclusion
Overview
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), formally Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP), are the FDA’s foundational framework to ensure products are safe, effective, and consistent. CGMP systems govern design, monitoring, and control across manufacturing processes and facilities for FDA‑regulated products (food, drugs, biologics, and medical devices). This article provides a practical, academically grounded overview aligned with dental industry expectations and the quality mindset embraced by FDA/ISO‑compliant organizations like XDENT LAB.
Introduction & Definition
CGMP refers to the FDA’s current standards for manufacturing quality that ensure a product is safe for use and contains the ingredients and strength it claims. The “current” modifier signals that expectations evolve with technology and contemporary best practices. CGMP establishes minimum requirements for methods, facilities, and controls used in manufacturing, packaging, labeling, storage, installation, and servicing of finished products.
Core Principles of FDA GMP
CGMP centers on modern, risk‑based, and system‑driven quality practices that adapt as technology advances.
The “Current” in CGMP
Regulations evolve with technology and standards.
Continuous improvement is expected (methods, controls, equipment).
Outdated systems risk non‑compliance.
Regulatory flexibility allows modernization.
Fundamental Requirements
CGMP requirements govern the methods, facilities, and controls for design, manufacture, packaging, labeling, storage, installation, and servicing of finished devices for human use—extending analogous principles to foods, drugs, and biologics.
Regulatory Framework
FDA enforces CGMP through codified regulations and direct inspections, backed by legal authority.

Legal Foundation
21 CFR Part 210–211: Pharmaceutical GMPs.
21 CFR Part 820: Medical Device Quality System Regulation (QSR).
21 CFR Part 110–117: Food GMPs.
21 CFR Part 600–680: Biological products.
21 CFR Part 225–226: Animal drug GMPs.
Facility inspections, surveillance, and for‑cause audits.
Warning letters, import alerts, seizures, injunctions.
Civil and criminal penalties for non‑compliance.
Mandatory adherence—CGMP is not voluntary.
Key GMP Requirements
CGMP emphasizes a comprehensive Quality Management System (QMS) spanning leadership, resources, processes, and monitoring.
Quality Management System
Management Responsibility: quality policy, organizational structure, resources, management review, quality planning.
Resource Management: personnel qualification, training, facility adequacy, equipment suitability, environmental controls.
Product Realization: design controls, purchasing controls, production planning, process validation, identification and traceability.
Measurement & Analysis: monitoring, data analysis, CAPA (corrective/preventive actions), continuous improvement.
Personnel Requirements
Defined education and competency standards.
Training documentation and ongoing qualification.
Responsibility for following procedures and reporting deviations.
Hygiene, cleanliness, and understanding of quality impact.
Facility & Equipment
Facilities: adequate space, robust construction, contamination prevention, environmental monitoring, maintenance programs.
Equipment: design/installation/operational/performance qualification; calibration programs.
Documentation Requirements
Documentation is the backbone of CGMP, ensuring traceability, consistency, and regulatory confidence.
Master Documentation
Quality manual and SOPs.
Master batch records and specifications.
Validation protocols and reports.
Version control, change management, controlled distribution.
Retention schedules and validated electronic systems.
Production Records
Manufacturing records and testing results.
Deviation and investigation reports.
Release documentation and batch disposition.
Traceability of raw materials, in‑process controls, final testing.
Distribution records and complaint files.
Process Control & Validation
Validation demonstrates that processes consistently produce products meeting predetermined specifications.
Process Validation
Process Design: knowledge gathering, process understanding, risk assessment, control strategy, scale‑up studies.
Process Qualification: equipment and facility qualification, performance qualification, process verification, documentation.
Continued Process Verification: ongoing monitoring, trend analysis, change control, revalidation triggers, improvement opportunities.
Change Control
Formal change identification and impact assessment.
Risk evaluation, approvals, implementation controls.
Effectiveness verification and post‑change monitoring.
Quality Control & Testing
Laboratory controls ensure identity, strength, quality, purity, and performance, supported by validated methods and calibrated equipment.

Laboratory Controls
Raw material, in‑process, and finished product testing.
Stability studies and environmental monitoring.
Method validation and reference standards.
Sample handling, chain of custody, and data reporting.
Specifications & Standards
Identity, strength/potency, and critical quality attributes.
Purity and performance characteristics.
Acceptance criteria grounded in science, statistics, and risk.
Patient safety as the defining constraint.
Compliance & Inspection
FDA verifies CGMP through inspections focused on system effectiveness and data integrity.
FDA Inspection Process
Pre‑approval, routine surveillance, for‑cause, and follow‑up inspections.
Post‑market surveillance and targeted reviews.
Focus on validation, change control, complaint handling, and data integrity.
Common Deficiencies
Inadequate procedures and poor documentation.
Validation gaps and ineffective training.
Deficient investigations and CAPA.
Data integrity concerns and contamination risks.
Process control failures and management oversight issues.
Industry‑Specific GMPs
While CGMP principles are universal, sector‑specific requirements tailor controls to product risk profiles.
Pharmaceutical GMPs (21 CFR 210–211)
Active ingredient control and cross‑contamination prevention.
Expiration dating, reserve samples, batch release.
Critical areas: sterile processing, water systems, HVAC, aseptic techniques.
Medical Device GMPs (21 CFR 820)
Design Controls: planning, inputs, outputs, reviews, verification/validation.
Production Controls: device master/history records, special processes, automation controls.
Food GMPs (21 CFR 110–117)
Sanitation controls and allergen management.
Supply chain verification and preventive controls.
HARPC requirements and hazard analysis.
Data Integrity in GMP
Trustworthy data underpins every CGMP element; ALCOA+ principles and electronic record controls are central.
ALCOA+ Principles
Attributable: who performed the activity.
Legible: clear and permanent.
Contemporaneous: recorded when performed.
Original: first capture source.
Accurate: error‑free.
Plus: complete, consistent, enduring, available.
Electronic Records (21 CFR Part 11)
System validation and audit trails.
Electronic signatures and access controls.
Data backup, retention, and disaster recovery.
Risk Management in GMP
Quality Risk Management embeds structured risk assessment and control within the QMS.
Quality Risk Management
Risk identification, analysis, evaluation.
Risk control and review cycles.
Integration with design, validation, and change control.
Tools & Methods
FMEA and HACCP.
Fault tree analysis.
Risk ranking matrices.
Statistical process control and capability analysis.
Training & Competency
Competent personnel ensure procedures are executed consistently and safely.
Training Programs
GMP fundamentals and job‑specific training.
Regulatory updates and safety procedures.
Quality awareness and culture.
Documentation
Training records and competency assessments.
Qualification matrices and retraining schedules.
Effectiveness evaluations.
Supplier Management
Robust supplier controls protect material quality and process consistency.
Vendor Qualification
Supplier audits and quality agreements.
Performance monitoring and risk assessment.
Continuous evaluation and approved supplier lists.
Control Measures
Incoming inspections and certificates of analysis.
Change notifications and quality metrics.
Traceability across the supply chain.
Continuous Improvement
Management reviews and CAPA propel sustained quality and regulatory resilience.
Management Review
Quality metrics, audit findings, and complaint trends.
Process performance and CAPA effectiveness.
Resource alignment and improvement roadmaps.
Improvement Initiatives
Process optimization and technology upgrades.
Training enhancements and system improvements.
Prudent innovation adoption.
Global Harmonization
CGMP aligns with international standards to support global quality and market access.

International Standards
ICH guidelines for pharmaceuticals.
ISO standards (e.g., ISO 13485 for devices, ISO 9001 for QMS).
WHO and PIC/S recommendations.
Regional regulations and mutual recognition.
Future of GMP
CGMP continues to evolve through technology and risk‑based oversight.
Emerging Trends
AI, continuous manufacturing, real‑time monitoring.
Predictive analytics and blockchain for traceability.
Quality metrics, patient‑centric design, supply chain integrity.
Sustainability and environmental considerations.
Implementation Best Practices
Building a GMP culture is a strategic commitment—more than meeting minimum requirements.
Building a GMP Culture
Leadership commitment and clear communication.
Employee engagement and accountability.
Continuous learning and resource allocation.
Training investment and recognition programs.
Common Pitfalls
Under‑resourcing and reactive approaches.
Poor documentation and siloed operations.
Compliance‑only focus without process robustness.
Conclusion
FDA’s CGMP provides a comprehensive, evolving framework to ensure the safety, quality, and efficacy of regulated products. Success depends on a strong quality culture, validated processes, reliable data, and continuous improvement. For dental practices and partners, aligning with FDA/ISO expectations builds trust and consistency across preventive and restorative workflows—exactly the philosophy behind XDENT LAB’s lab‑to‑lab services and quality systems.
XDENT LAB is an expert in Lab-to-Lab Full Service from Vietnam, with the signature services of Removable & Implant, meeting U.S. market standards – approved by FDA & ISO. Founded in 2017, XDENT LAB has grown from local root to global reach, scaling with 2 factories and over 100 employees.. Our state-of-the-art technology, certified technicians, and commitment to compliance make us the trusted choice for dental practices looking to ensure quality and consistency in their products.
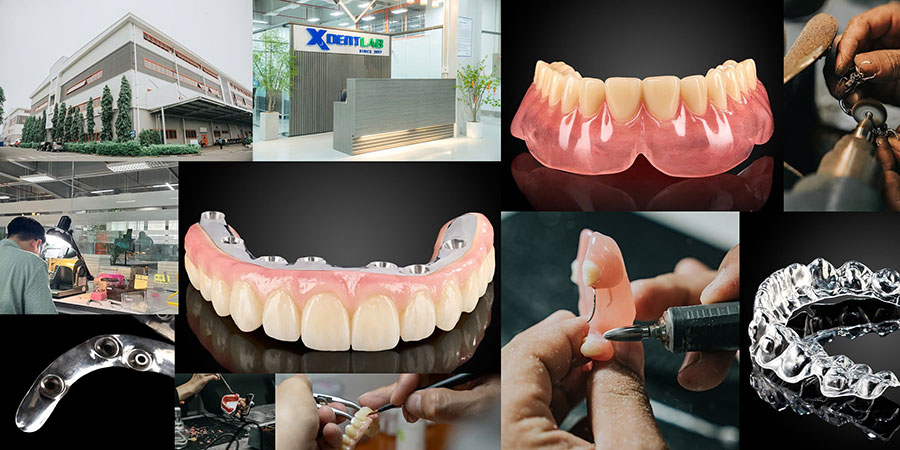
Our commitments are:
100% FDA-Approved Materials.
Large-Scale Manufacturing, high volume, remake rate < 1%.
2~3 days in lab (*digital file).
Your cost savings 30%.
Uninterrupted Manufacturing 365 days a year.
Contact us today to establish a strategy to reduce operating costs.
--------❃--------
Vietnam Dental Laboratory - XDENT LAB
🏢 Factory 1: 95/6 Tran Van Kieu Street, Binh Phu Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
🏢 Factory 2: Kizuna 3 Industrial Park, Can Giuoc Commune, Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam
☎ Hotline: 0919 796 718 📰 Get detailed pricing
Share this post: