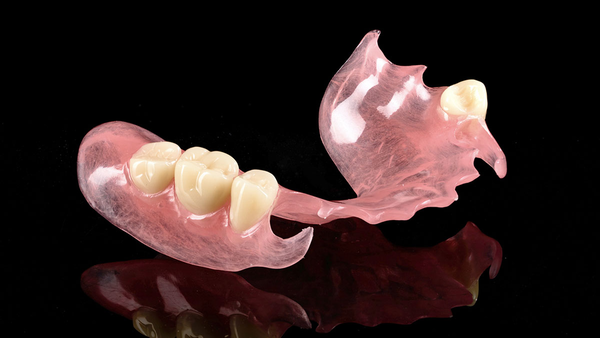
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) has emerged as a cornerstone material in modern dental laboratories, thanks to its versatility, superior properties, and adaptability to both traditional and digital workflows. This synthetic polymer is widely used for fabricating provisional restorations, denture bases, and various other dental prosthetic applications.

Table of contents [Show]
- What is PMMA?
- Chemical Composition and Structure
- Manufacturing Methods in Dental Labs
- Material Properties of PMMA
- Clinical Applications of PMMA
- Advantages of PMMA Over Traditional Materials
- Processing Techniques for PMMA
- Biological Compatibility
- Economic and Laboratory Efficiency
- Limitations and Considerations
- Recent Innovations and Future Directions
- Conclusion
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) has emerged as a cornerstone material in modern dental laboratories, thanks to its versatility, superior properties, and adaptability to both traditional and digital workflows. This synthetic polymer is widely used for fabricating provisional restorations, denture bases, and various other dental prosthetic applications. Its exceptional durability, aesthetics, and biocompatibility make it the material of choice for long-term provisional restorations and beyond.
In this article, we will explore the chemical composition, manufacturing methods, material properties, clinical applications, advantages, and future developments of PMMA in dental laboratory applications.

What is PMMA?
PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) is a thermoplastic synthetic polymer known for its exceptional optical, physical, and mechanical properties. It is widely regarded as a reliable material for dental prosthetics, especially in provisional restorations, due to its ability to replicate the natural appearance of teeth while offering excellent strength and biocompatibility.
PMMA is available in various forms, including pre-polymerized blocks for CAD/CAM milling and traditional powder-liquid systems for manual processing. These options make it a versatile material for dental laboratories catering to diverse clinical needs.
Chemical Composition and Structure
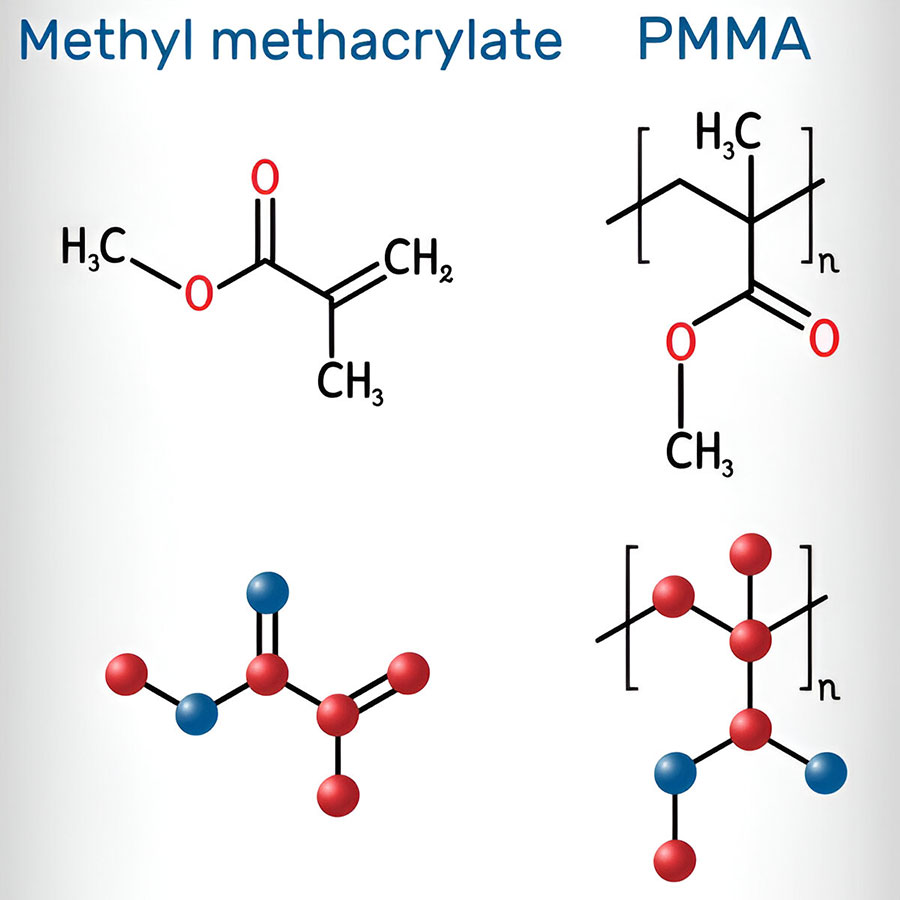
Molecular Structure
PMMA consists of a linear polymer chain of methyl methacrylate units.
Chemical formula: (C5O2H8)n.
It has an amorphous thermoplastic structure, with cross-linked variants available for enhanced mechanical and thermal properties.
Polymerization Process
PMMA is synthesized through free radical polymerization, which can be:
Heat-cured.
Cold-cured.
Light-cured.
Pre-polymerized PMMA blocks are factory-manufactured under optimal conditions, resulting in minimal residual monomer content and superior material properties.
Manufacturing Methods in Dental Labs
PMMA can be processed using both traditional techniques and digital workflows, depending on the specific application and the lab's capabilities.
CAD/CAM Milling
Pre-polymerized PMMA blocks: Manufactured under controlled conditions for consistent quality.
Multi-layered pucks: Offer natural color gradation for enhanced aesthetics.
Dense structure: Eliminates porosity issues associated with traditional processing.
Precision milling: Ensures accurate fit, reducing the need for manual adjustments.
Traditional Processing
Powder-liquid mixing systems: Commonly used for denture base fabrication.
Heat polymerization: Produces durable and stable prosthetics.
Pressure pot curing: Reduces porosity and enhances mechanical properties.
Injection molding systems: Provides uniform material distribution and improved strength.
Material Properties of PMMA
PMMA’s properties make it an ideal choice for a wide range of dental applications:
Physical Properties
Density: 1.17-1.20 g/cm³.
Flexural strength: 80-120 MPa.
Elastic modulus: 2.4-3.4 GPa.
Hardness: 15-20 Vickers.
Water absorption: <32 μg/mm³.
Mechanical Advantages
Superior fracture resistance compared to traditional acrylics.
Excellent dimensional stability with minimal polymerization shrinkage.
High impact strength and good fatigue resistance.
Optical Properties
Translucency: Mimics the natural appearance of teeth.
Color stability: Maintains aesthetics over time.
Available in multiple shades and can be further characterized with stains.
Clinical Applications of PMMA
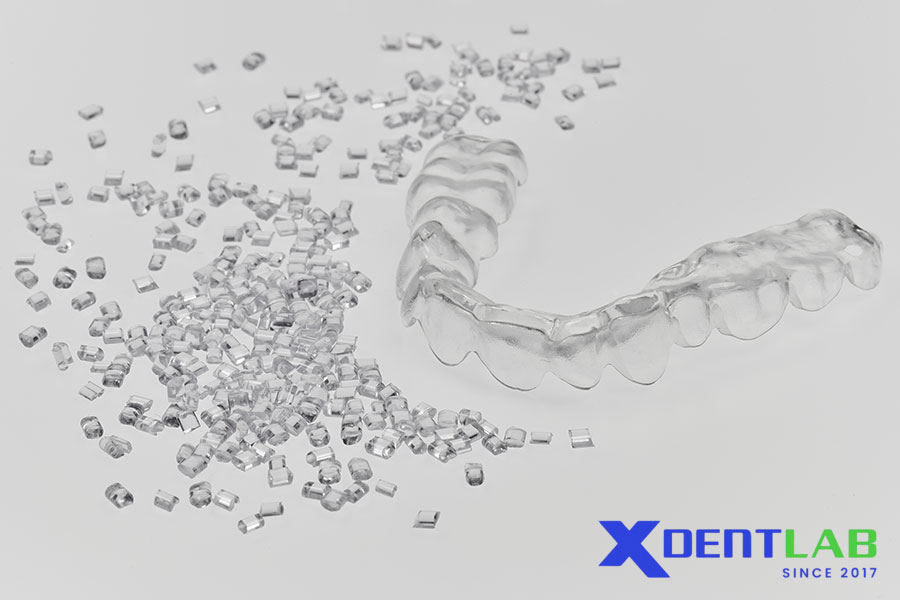

PMMA is extensively used in dental laboratories for a variety of clinical applications:
Provisional Restorations
Long-term provisionals: Ideal for cases requiring extended healing periods.
Implant provisionals: Used during the osseointegration phase.
Full-mouth rehabilitation: Temporary restorations to manage complex cases.
Diagnostic restorations: Testing new vertical dimensions or occlusal schemes.
Specific Uses
Single crowns and multi-unit bridges.
Implant-supported provisional restorations.
Immediate loading protocols.
Orthodontic appliances, occlusal splints, and night guards.
Advantages of PMMA Over Traditional Materials
Compared to Bis-acryl Composites
Better long-term color stability.
Superior polishability for a natural finish.
More cost-effective for extended wear.
Easier to repair and adjust.
Compared to Hand-Processed Acrylics
Eliminates porosity issues, reducing bacterial adhesion.
Provides better marginal integrity.
Offers consistent material properties.
Minimizes technique sensitivity during fabrication.
Processing Techniques for PMMA
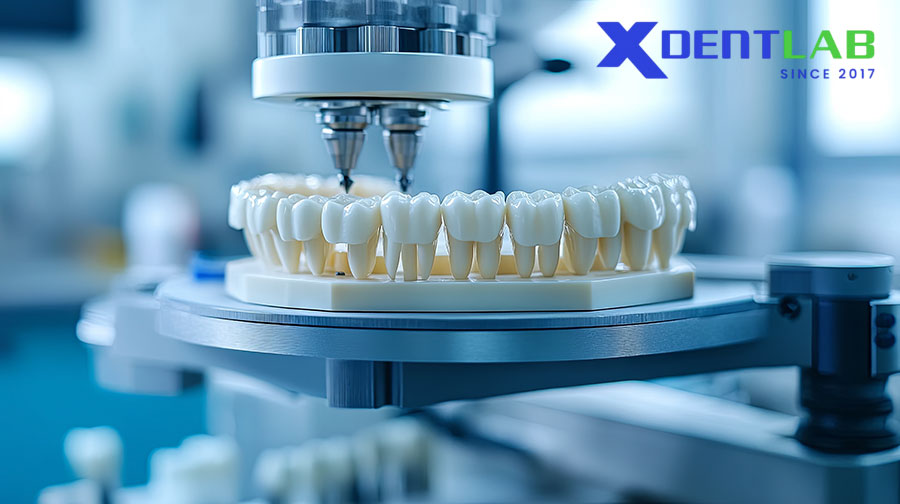

CAD/CAM Workflow
Digital impressions or scans.
Design using CAD software.
Milling from pre-polymerized PMMA blocks.
Finishing, polishing, and optional characterization.
Surface Treatment
Diamond polishing for a high-gloss finish.
Glazing options for enhanced aesthetics.
Staining to achieve lifelike characterization.
Biological Compatibility
PMMA is highly biocompatible, making it a safe choice for dental restorations:
Biocompatibility Features
Low residual monomer content (<1%) minimizes tissue irritation.
Non-allergenic for most patients.
Promotes a good soft tissue response.
Reduces plaque accumulation, ensuring better oral health outcomes.
Patient Safety
FDA-approved formulations and CE-marked products.
Extensive clinical history and documented safety profiles.
Economic and Laboratory Efficiency
Cost-Effectiveness
Moderate material cost compared to ceramics.
Reduced chair time due to streamlined workflows.
Extended service life, reducing the need for remakes.
Laboratory Efficiency
Digital workflows reduce manual labor.
Predictable outcomes with minimal adjustments.
Lower labor costs due to automation.
Limitations and Considerations
While PMMA offers numerous advantages, it does have limitations:
Material Limitations
Not suitable for permanent restorations.
Lower strength compared to ceramics.
Prone to wear in patients with bruxism.
Potential for color changes with staining foods or beverages.
Clinical Limitations
Maximum recommended wear time: 6-12 months.
Regular monitoring is required.
Limited use in high-stress areas or patients with severe parafunctions.
Recent Innovations and Future Directions

Advanced PMMA Formulations
Nano-filled PMMA: Enhanced strength and wear resistance.
Fiber-reinforced PMMA: Improved mechanical properties.
Antimicrobial additives: Reduce bacterial colonization.
Self-glazing formulations: Eliminate the need for polishing.
Digital Integration
3D printing for customized prosthetics.
Multi-color milling blocks for lifelike aesthetics.
AI-assisted design optimization for faster workflows.
Future Developments
Bioactive PMMA materials to promote tissue healing.
Self-healing polymers for enhanced durability.
Smart materials with color indicators for wear assessment.
Sustainable manufacturing processes to reduce environmental impact.
Conclusion
PMMA has revolutionized dental laboratory workflows, offering a reliable, efficient, and cost-effective solution for provisional restorations and other prosthetic applications. Its versatility, combined with modern digital technologies like CAD/CAM and 3D printing, ensures consistent quality and superior clinical outcomes.
As a leader in dental lab services, XDENT LAB leverages state-of-the-art technology and expertise to deliver PMMA-based solutions that meet the highest standards of quality and compliance. With ongoing advancements in PMMA formulations and processing methods, XDENT LAB is committed to helping dental practices achieve predictable, long-lasting results for their patients.
XDENT LAB is an expert in Lab-to-Lab Full Service from Vietnam, with the signature services of Removable & Implant, meeting U.S. market standards – approved by FDA & ISO. Founded in 2017, XDENT LAB has grown from local root to global reach, scaling with 2 factories and over 100 employees.. Our state-of-the-art technology, certified technicians, and commitment to compliance make us the trusted choice for dental practices looking to ensure quality and consistency in their products.
Our commitments are:
100% FDA-Approved Materials.
Large-Scale Manufacturing, high volume, remake rate < 1%.
2~3 days in lab (*digital file).
Your cost savings 30%.
Uninterrupted Manufacturing 365 days a year.
Contact us today to establish a strategy to reduce operating costs.
--------❃--------
Vietnam Dental Laboratory - XDENT LAB
🏢 Factory 1: 95/6 Tran Van Kieu Street, Binh Phu Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
🏢 Factory 2: Kizuna 3 Industrial Park, Can Giuoc Commune, Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam
☎ Hotline: 0919 796 718 📰 Get detailed pricing
Share this post: