Ceramic frameworks represent a transformative advancement in restorative dentistry, offering exceptional aesthetics, biocompatibility, and durability. These materials have evolved to meet diverse clinical demands, providing solutions for both functional and aesthetic challenges.
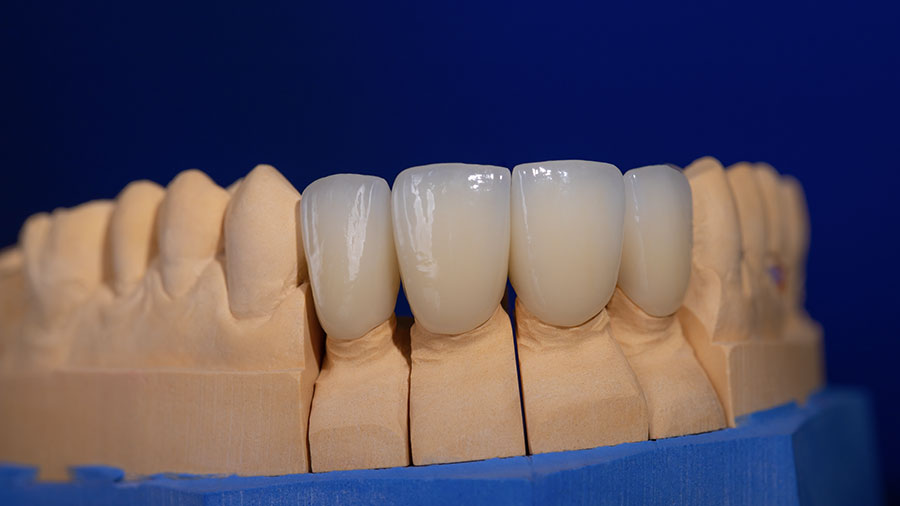
Table of contents [Show]
Ceramic frameworks represent a transformative advancement in restorative dentistry, offering exceptional aesthetics, biocompatibility, and durability. These materials have evolved to meet diverse clinical demands, providing solutions for both functional and aesthetic challenges. This article explores the types, properties, applications, and future trends of ceramic frameworks, offering dental practices a guide to optimizing treatment outcomes.

Introduction and Classification
Ceramic frameworks are widely used for dental restorations due to their ability to mimic natural tooth structure while ensuring long-term performance. A classification system for ceramic materials aids in clinical decision-making, communication, and education. Ceramic frameworks can be broadly divided into two main categories: Glass-Ceramics and Polycrystalline Ceramics, each suited to specific applications.
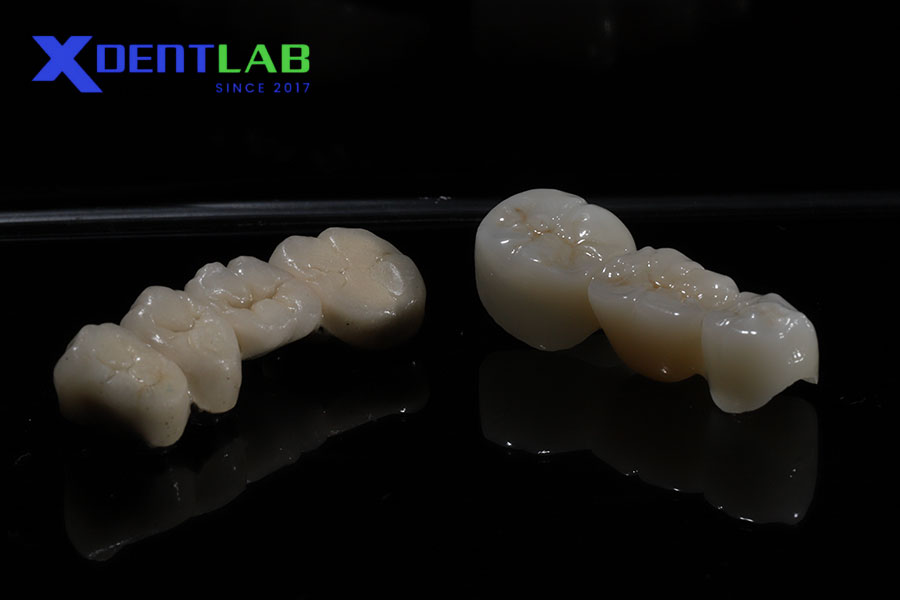
Types of Ceramic Frameworks
Glass-Ceramics
Glass-ceramics are renowned for their superior aesthetics and translucency, making them ideal for anterior restorations.
Key Types:
Lithium Disilicate (e.max)
Fabricated using CAD/CAM or ceramic-press methods.
Offers high strength and translucency for crowns, veneers, and bridges.
Leucite-Reinforced Ceramics
Primarily used for veneers and anterior crowns due to their aesthetic properties.
Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate
Combines the strength of zirconia with the aesthetics of glass-ceramics.
Polycrystalline Ceramics
Polycrystalline ceramics are high-strength materials designed for load-bearing restorations, particularly in posterior teeth.
Key Types:
Zirconia (Y-TZP)
Exceptional strength and biocompatibility.
Ideal for posterior crowns, bridges, and implant-supported restorations.
Alumina
Used for anterior crowns and veneers due to its natural luster and color.
Zirconia-Toughened Alumina (ZTA)
New formulations with alumina/zirconia ratios (e.g., 80/20, 70/30) offer enhanced flexural strength.
Properties and Characteristics

Mechanical Properties
Glass-Ceramics
Varying strength and thermal properties based on composition.
Lithium disilicate demonstrates high fatigue resistance when luted with self-adhesive resin cements.
Polycrystalline Ceramics
Zirconia provides superior material strength and fracture resistance.
Aesthetic Properties
Glass-Ceramics: Known for translucency and ability to mimic enamel.
Polycrystalline Ceramics: Zirconia can be layered with veneering ceramics for enhanced aesthetics.
Clinical Applications
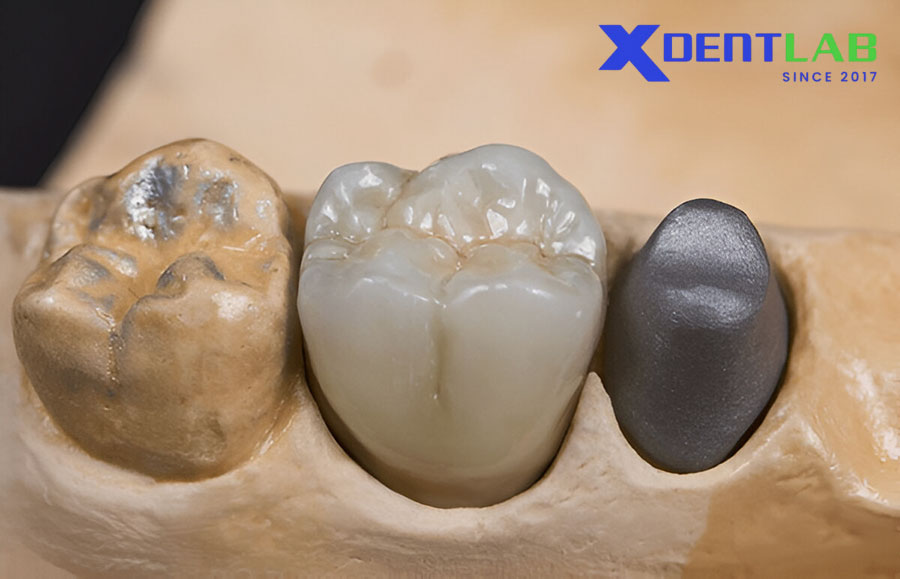
Ceramic frameworks are versatile and used in a variety of restorative procedures:
Single-Tooth Restorations: Crowns, inlays, and onlays.
Multi-Unit Restorations: Bridges (limited by material strength).
Complex Cases: Full-mouth rehabilitations.
Veneers: Glass-ceramics are preferred for their aesthetic appeal.
Indications and Contraindications
Indications
Anterior Restorations: Glass-ceramics and alumina for optimal aesthetics.
Posterior Restorations: Zirconia and lithium disilicate for strength and durability.
Short-Span Bridges: Zirconia frameworks for load-bearing areas.
Partial Coverage Restorations: Glass-ceramics for conservative preparations.
Contraindications
Long-Span Bridges: Limited to high-strength ceramics like zirconia.
Bruxism Patients: Requires careful material selection to withstand occlusal forces.
Insufficient Tooth Structure: May compromise bonding and restoration success.
Framework Design Considerations
Successful ceramic restorations rely on collaboration between the dentist and dental technician.
Key considerations include:
Material Selection: Based on location, function, and patient factors.
Minimum Thickness: Varies by material to ensure strength and aesthetics.
Stress Distribution: Optimized design to prevent fractures.
Processing Methods
CAD/CAM Technology
Digital workflows enable precise fabrication of ceramic frameworks:
Lithium Disilicate: Processed via CAD/CAM or press techniques.
Zirconia: Primarily milled using CAD/CAM for accuracy.
Traditional Methods
Press Ceramics: Used for certain glass-ceramic systems.
Layering Techniques: For veneering ceramics to enhance aesthetics.
Clinical Considerations
Cementation
Proper cementation protocols are crucial for long-term success:
Self-Adhesive Resin Cements: Recommended for lithium disilicate restorations.
Surface Treatments: Required for zirconia to improve bonding.
Limitations
While ceramic frameworks provide reliable performance, limitations include:
Material Selection: Must consider functional and aesthetic demands.
Processing Challenges: Zirconia cores may require specialized equipment.
Future Developments

The field of ceramic frameworks continues to evolve, with innovations aimed at improving performance and clinical outcomes:
New Ceramic Formulations: Combining strength and aesthetics for versatile applications.
Enhanced Processing Techniques: Faster and more precise manufacturing methods.
Improved Bonding Protocols: Ensuring long-term restoration success.
Hybrid Materials: Combining ceramics with other materials for superior performance.
Conclusion
Ceramic frameworks are integral to modern dentistry, offering unmatched aesthetics, strength, and biocompatibility. Understanding the composition, properties, and clinical applications of different ceramic materials is essential for successful treatment planning and execution.
At XDENT LAB, we specialize in crafting high-quality ceramic frameworks using state-of-the-art technology and FDA-approved processes. Whether you need glass-ceramics for anterior restorations or zirconia frameworks for posterior applications, our expert technicians ensure precision and consistency in every product.
Contact XDENT LAB today to learn how our lab-to-lab services can elevate your dental practice and deliver exceptional results for your patients!
XDENT LAB is an expert in Lab-to-Lab Full Service from Vietnam, with the signature services of Removable & Implant, meeting U.S. market standards – approved by FDA & ISO. Founded in 2017, XDENT LAB has grown from local root to global reach, scaling with 2 factories and over 100 employees.. Our state-of-the-art technology, certified technicians, and commitment to compliance make us the trusted choice for dental practices looking to ensure quality and consistency in their products.
Our commitments are:
100% FDA-Approved Materials.
Large-Scale Manufacturing, high volume, remake rate < 1%.
2~3 days in lab (*digital file).
Your cost savings 30%.
Uninterrupted Manufacturing 365 days a year.
Contact us today to establish a strategy to reduce operating costs.
--------❃--------
Vietnam Dental Laboratory - XDENT LAB
🏢 Factory 1: 95/6 Tran Van Kieu Street, Binh Phu Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
🏢 Factory 2: Kizuna 3 Industrial Park, Can Giuoc Commune, Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam
☎ Hotline: 0919 796 718 📰 Get detailed pricing
Share this post: