Zirconia-based ceramics, especially yttrium-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP), have revolutionized restorative dentistry since their introduction in the early 2000s. These advanced materials offer mechanical properties up to three times higher than other all-ceramic systems, making them suitable for clinical situations previously dominated by metal-ceramic restorations.
Table of contents [Show]
- Material Science and Crystallography
- Types of Dental Zirconia Systems
- Manufacturing and Processing
- Mechanical Properties
- Surface Modifications and Bonding
- Clinical Applications
- Clinical Performance
- Advantages and Limitations
- Current Developments
- Future Perspectives
- Clinical Recommendations
- Conclusion
Zirconia-based ceramics, especially yttrium-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP), have revolutionized restorative dentistry since their introduction in the early 2000s. These advanced materials offer mechanical properties up to three times higher than other all-ceramic systems, making them suitable for clinical situations previously dominated by metal-ceramic restorations. The evolution of zirconia from opaque frameworks to highly translucent monolithic restorations has expanded its clinical applications for both anterior and posterior restorations, combining strength, aesthetics, and versatility.

Material Science and Crystallography
Phase Transformations
Zirconia exists in three crystallographic phases:
Monoclinic (m): Stable at room temperature up to 1170°C.
Tetragonal (t): Stable between 1170°C and 2370°C, critical for dental applications due to its transformation toughening mechanism.
Cubic (c): Stable above 2370°C, contributing to translucency in high-end zirconia systems.
The stress-induced transformation from tetragonal to monoclinic phase creates compressive stresses that prevent crack propagation, significantly enhancing fracture toughness.
Stabilization Mechanisms
To retain the tetragonal phase at room temperature, stabilizing oxides such as yttria (Y₂O₃) are added. The type and concentration of stabilizer determine the zirconia’s phase composition, translucency, and mechanical properties:
3 mol% Y₂O₃: Predominantly tetragonal, high strength.
4-5 mol% Y₂O₃: Mixed tetragonal-cubic, improved translucency.
>8 mol% Y₂O₃: Fully cubic, highest translucency but reduced strength.
Types of Dental Zirconia Systems
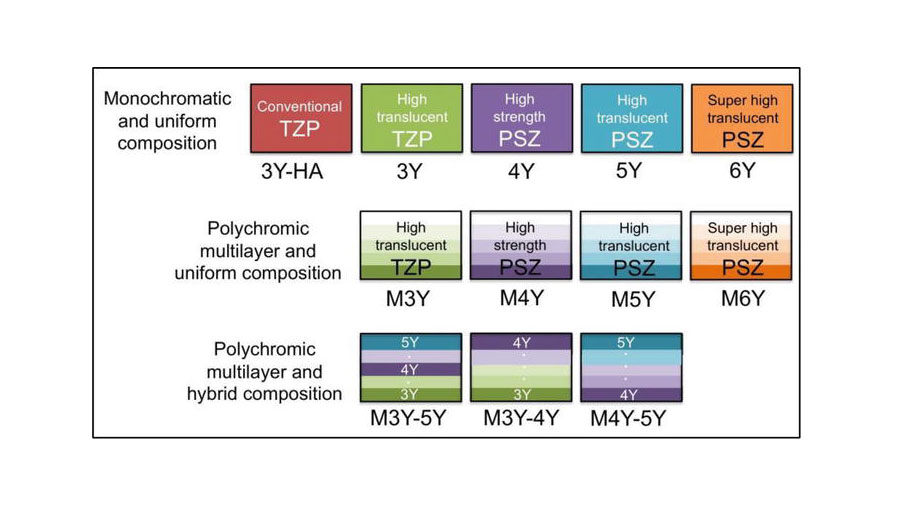
First Generation: 3Y-TZP
This traditional zirconia system offers exceptional mechanical properties:
Flexural strength: 900-1200 MPa.
Fracture toughness: 5-10 MPa·m^½.
Applications: Posterior crowns, bridges, implant abutments.
Second Generation: High-Translucency Zirconia
Developed to address aesthetic limitations:
4Y-PSZ and 5Y-PSZ: Higher cubic phase content for improved translucency.
Applications: Anterior restorations requiring natural aesthetics.
Third Generation: Multi-Layered Zirconia
Innovative gradient technology combines strength, translucency, and aesthetics in a single block:
Strength gradient: Higher in cervical areas, lower in incisal regions.
Color gradient: Mimics natural tooth appearance.
Manufacturing and Processing
Powder Synthesis
Zirconia powders are produced using methods such as co-precipitation and sol-gel processing, ensuring high purity and uniform particle size for optimal properties.
Green Body Formation
Pre-sintered blanks are formed using techniques like uniaxial pressing, cold isostatic pressing, or injection molding, providing the foundation for CAD/CAM fabrication.
Sintering Process
Sintering at temperatures between 1450-1550°C ensures high density (>99.5%), controlled grain growth (<1 μm), and minimal shrinkage.
CAD/CAM Processing
Two approaches are commonly used:
Soft Machining: Pre-sintered blanks, easier to machine, compensates for shrinkage during sintering.
Hard Machining: Fully sintered blocks, higher precision but increased tool wear.
Mechanical Properties
Strength and Toughness
Zirconia systems exhibit:
Flexural Strength: 3Y-TZP > 900 MPa; 5Y-PSZ ~ 600 MPa.
Fracture Toughness: Enhanced by transformation toughening.
Aging and Degradation
Low-temperature degradation (LTD) can occur due to moisture exposure, leading to surface phase transformation. Preventive measures include adding alumina and optimizing grain size.
Surface Modifications and Bonding
Surface Treatments
Methods like air abrasion and tribochemical coating improve bonding by creating micro-retentions and enabling silanization.
Chemical Bonding
Primers containing MDP (10-Methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate) form strong chemical bonds with zirconia, ensuring long-term stability.
Clinical Applications
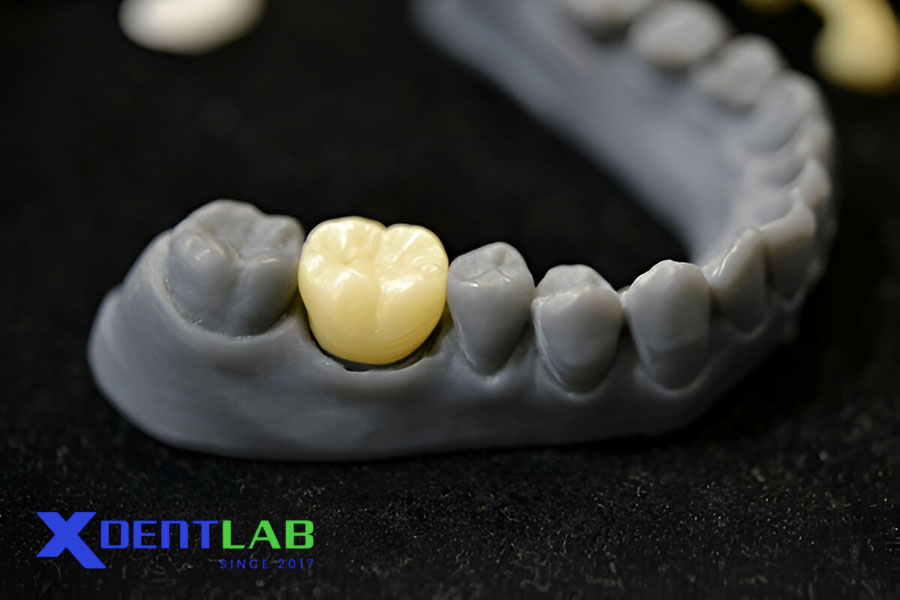
Crown and Bridge Frameworks
Zirconia frameworks are ideal for posterior crowns and multi-unit bridges due to their strength and durability.
Monolithic Restorations
Monolithic zirconia eliminates chipping risks and simplifies fabrication, making it cost-effective and predictable.
Implant Applications
Zirconia abutments and hybrid designs offer superior aesthetics and soft tissue compatibility.
Clinical Performance
Success Rates
Zirconia restorations show high survival rates (>95% at 5 years) with minimal complications.
Failure Analysis
Common issues include veneer chipping and framework fractures, often preventable with proper design and processing.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
Exceptional strength and toughness.
Superior biocompatibility.
Metal-free aesthetics.
Versatility in applications.
Limitations
Requires specialized bonding protocols.
Potential for low-temperature degradation.
Higher cost compared to metal-ceramic systems.
Current Developments
Material Innovations
Advances like ultra-translucent zirconia and functionally graded materials are pushing boundaries in aesthetics and performance.
Processing Advances
Speed sintering and additive manufacturing are streamlining production processes and enabling customization.
Future Perspectives
Research Directions
Exploration into novel compositions, antibacterial coatings, and smart materials promises exciting developments in zirconia systems.
Clinical Trends
Digital workflows and minimally invasive techniques are shaping the future of zirconia applications in restorative dentistry.
Clinical Recommendations
Material Selection
Choose zirconia type based on clinical needs:
Posterior restorations: 3Y-TZP for maximum strength.
Anterior restorations: 5Y-PSZ for translucency and aesthetics.
Cementation Protocols
Follow evidence-based guidelines:
Use MDP-based adhesives.
Prepare surfaces with air abrasion and cleaning.
Conclusion
Zirconia-based systems are transforming restorative dentistry, offering unmatched mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and aesthetics. As innovations continue, zirconia remains a cornerstone of modern dental frameworks. XDENT LAB leverages state-of-the-art technology and expertise to deliver high-quality zirconia solutions, ensuring consistent results for dental practices worldwide.
XDENT LAB is an expert in Lab-to-Lab Full Service from Vietnam, with the signature services of Removable & Implant, meeting U.S. market standards – approved by FDA & ISO. Founded in 2017, XDENT LAB has grown from local root to global reach, scaling with 2 factories and over 100 employees.. Our state-of-the-art technology, certified technicians, and commitment to compliance make us the trusted choice for dental practices looking to ensure quality and consistency in their products.
Our commitments are:
100% FDA-Approved Materials.
Large-Scale Manufacturing, high volume, remake rate < 1%.
2~3 days in lab (*digital file).
Your cost savings 30%.
Uninterrupted Manufacturing 365 days a year.
Contact us today to establish a strategy to reduce operating costs.
--------❃--------
Vietnam Dental Laboratory - XDENT LAB
🏢 Factory 1: 95/6 Tran Van Kieu Street, Binh Phu Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
🏢 Factory 2: Kizuna 3 Industrial Park, Can Giuoc Commune, Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam
☎ Hotline: 0919 796 718 📰 Get detailed pricing
Share this post: