Uncover the innovative benefits of glass ionomer cements in caries prevention. XDENT LAB provides certified dental lab outsourcing solutions for consistent quality.
Table of contents [Show]
- Introduction to Glass Ionomer Cements
- Composition and Chemistry
- Fluoride Release Mechanisms
- Fluoride Recharge Capability
- Preventive Effects and Clinical Applications
- Types of Glass Ionomer Cements
- Clinical Applications in Prevention
- Enhancement Strategies
- Comparative Effectiveness
- Limitations and Challenges
- Recent Innovations and Future Directions
- Evidence-Based Recommendations
- Conclusion
Introduction to Glass Ionomer Cements
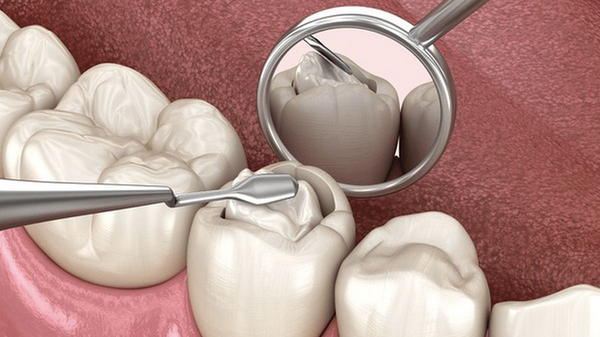
Glass ionomer cements (GICs) are a unique and versatile class of dental materials that combine restorative and preventive properties. Their ability to release fluoride over time makes them invaluable tools in caries prevention strategies. By reducing the size and viability of oral bacteria populations, GICs help protect teeth from decay. Since their introduction, GICs have undergone significant advancements, with modern formulations offering improved physical properties while retaining their characteristic fluoride-releasing benefits.
Composition and Chemistry
Basic Components
Glass ionomer cements are composed of:
Fluoroaluminosilicate glass powder: Provides fluoride ions for release.
Polyacrylic acid or copolymer acids: React with the glass powder to form the cement matrix.
Water: Acts as the medium for the acid-base reaction.
Tartaric acid: Modifies the reaction, improving working and setting times.
Fluoride: Incorporated into the glass structure for long-term release.
Setting Reaction
The setting process involves an acid-base reaction between the polyacid and the fluoroaluminosilicate glass:
The acid dissolves the glass particles.
Metal ions (such as calcium, aluminum, and fluoride) are released.
These ions react with the polyacid to form a polyacrylate salt matrix.
The material continues to mature over weeks to months, forming a durable structure with a long-lasting fluoride reservoir.
Fluoride Release Mechanisms
Primary Release Phase
The initial fluoride release is characterized by:
A burst release within the first 24-48 hours.
Fluoride ions dissolving from the surface of glass particles.
Diffusion through the hydrogel matrix.
pH-dependence, with higher release in acidic conditions (ideal for caries-prone environments).
Long-term Release Patterns
After the initial phase, GICs provide sustained fluoride release over months or even years through:
Diffusion-controlled release of fluoride ions.
Matrix permeability, allowing slow release over time.
Environmental factors such as pH and temperature influencing release rates.
Fluoride Recharge Capability
Recharge Mechanisms
One of the most beneficial properties of GICs is their ability to recharge fluoride from external sources, including:
Topical fluoride treatments.
Fluoride-containing toothpastes and mouthwashes.
Fluoridated water.
Adjacent fluoride-releasing materials.
Clinical Significance of Recharge
The ability to recharge fluoride enhances the longevity of GICs' preventive effects by:
Renewing fluoride release after initial depletion.
Building a cumulative fluoride reservoir in the material.
Enhancing protection against caries over time.
Complementing other preventive measures such as fluoride varnishes and sealants.
Preventive Effects and Clinical Applications
Caries Prevention Efficacy
Clinical studies show that GIC sealants can reduce caries risk by up to 76%, particularly on occlusal fissure surfaces.
Fluoride released from GICs can diffuse into adjacent enamel, providing additional protection to nearby tooth structures.
Remineralization Properties
GICs promote remineralization by:
Facilitating fluoride uptake in adjacent enamel.
Strengthening enamel to resist demineralization.
Creating fluoride-enriched zones that protect against acid attacks.
Types of Glass Ionomer Cements
Conventional GICs
Features:
High fluoride release rates.
Chemical adhesion to enamel and dentin.
Biocompatibility and moisture tolerance.
Limited mechanical strength compared to composites and amalgam.
Resin-Modified GICs (RMGICs)
Features:
Added resin components for light-curing and improved strength.
Better handling and moisture control during placement.
Maintains fluoride release properties.
High-Viscosity GICs
Features:
Enhanced powder-liquid ratio for improved strength.
Suitable for Atraumatic Restorative Treatment (ART).
Better wear resistance while maintaining fluoride release.
Clinical Applications in Prevention

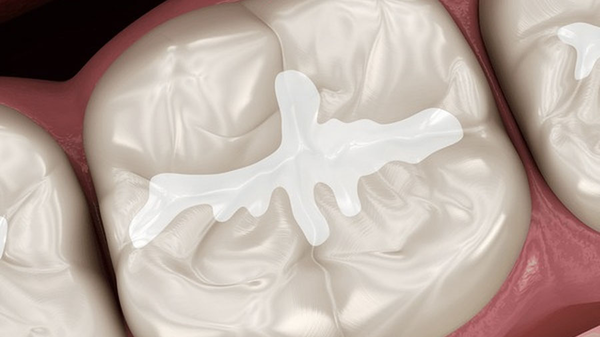
Pit and Fissure Sealants
GIC sealants are ideal for:
Preventing occlusal caries in children and high-risk patients.
Releasing fluoride directly into fissures.
Retaining effectiveness even with partial sealant loss.
Preventive Restorations
Applications include:
Minimal intervention dentistry techniques.
Tunnel restorations and preventive resin restorations (PRR).
Restorative solutions for high-risk surfaces.
Orthodontic Applications
GICs are commonly used in orthodontics for:
Band and bracket cementation with fluoride release.
Preventing white spot lesions around brackets.
Minimizing decalcification risks during orthodontic treatment.
Enhancement Strategies
Nanoparticle Modifications
Recent advancements include the addition of nanoparticles (e.g., titanium dioxide) to improve:
Fluoride release and recharge capabilities.
Mechanical properties and durability.
Antimicrobial effects and biocompatibility.
Bioactive Glass Additions
Incorporating bioactive glass into GICs enhances:
Ion release and remineralization potential.
Integration with natural tooth structure.
Synergistic effects for caries prevention.
Comparative Effectiveness
Versus Other Fluoride-Releasing Materials
GICs release fluoride for longer durations compared to composites and varnishes.
They offer chemical bonding to tooth structure, reducing technique sensitivity.
Unlike varnishes, GICs provide continuous fluoride delivery rather than episodic application.
Clinical Performance Studies
Research highlights include:
Effective caries prevention in high-risk populations.
Reduced risk of secondary caries around restorations.
Cost-effective solutions for long-term caries management.
Limitations and Challenges
Material Properties
Lower mechanical strength compared to composites and amalgam.
Moisture sensitivity during placement.
Limited aesthetic properties in certain formulations.
Clinical Challenges
Proper case selection and patient education are critical.
Maintenance and fluoride recharge protocols must be followed.
Longevity may be limited in high-stress areas.
Recent Innovations and Future Directions
Smart GIC Materials
Developments include:
pH-responsive fluoride release.
Enhanced recharge capabilities.
Improved mechanical and aesthetic properties.
Nanotechnology and 3D Printing
Nanoscale modifications for optimized fluoride release and antimicrobial properties.
3D-printed GICs for personalized and precise preventive restorations.
Evidence-Based Recommendations
Clinical Guidelines
Use GICs for high caries-risk patients, pediatric, and geriatric cases.
Implement regular fluoride recharge protocols.
Combine GICs with other preventive measures for maximum efficacy.
Best Practices
Ensure proper isolation and material handling during placement.
Educate patients about fluoride benefits and maintenance.
Schedule regular recall appointments for long-term monitoring.
Conclusion
Glass ionomer cements are a cornerstone of fluoride-based preventive dentistry, offering a unique combination of restorative and preventive benefits. Their ability to release and recharge fluoride makes them a powerful tool for caries prevention, particularly in high-risk populations. While they have limitations in mechanical properties, ongoing innovations such as nanoparticle enhancements and smart materials are addressing these challenges. With evidence-based applications and a focus on quality assurance, GICs continue to play a vital role in modern preventive dentistry.
At XDENT LAB, we are committed to supporting dental practices with high-quality lab-to-lab services, ensuring consistency and compliance in all dental restorations. Trust us to deliver world-class dental solutions tailored to your practice's needs.
XDENT LAB is an expert in Lab-to-Lab Full Service from Vietnam, with the signature services of Removable & Implant, meeting U.S. market standards – approved by FDA & ISO. Founded in 2017, XDENT LAB has grown from local root to global reach, scaling with 2 factories and over 100 employees.. Our state-of-the-art technology, certified technicians, and commitment to compliance make us the trusted choice for dental practices looking to ensure quality and consistency in their products.
Our commitments are:
100% FDA-Approved Materials.
Large-Scale Manufacturing, high volume, remake rate < 1%.
2~3 days in lab (*digital file).
Your cost savings 30%.
Uninterrupted Manufacturing 365 days a year.
Contact us today to establish a strategy to reduce operating costs.
--------❃--------
Vietnam Dental Laboratory - XDENT LAB
🏢 Factory 1: 95/6 Tran Van Kieu Street, Binh Phu Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
🏢 Factory 2: Kizuna 3 Industrial Park, Can Giuoc Commune, Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam
☎ Hotline: 0919 796 718 📰 Get detailed pricing
Share this post: